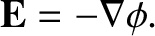Poisson's Equation
We have seen that the electric field generated by a set of stationary charges can be written as
the gradient of a scalar potential, so that
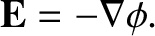 |
(2.98) |
[See Equation (2.17).]
The previous equation can be combined with the field equation (2.54) to give a partial
differential equation for the scalar potential:
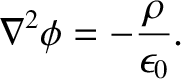 |
(2.99) |
(See Section A.21.)
This equation is known
as Poisson's equation. (See Section 1.8.5.)