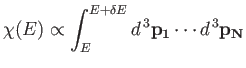

Next: Exercises
Up: Statistical Mechanics
Previous: Probability Calculations
Behavior of Density of States
Consider an
isolated system in equilibrium whose volume is 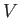 , and whose energy lies in the
range
, and whose energy lies in the
range 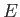 to
to
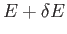 .
Let
.
Let
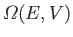 be the total number of microscopic states that
satisfy these constraints.
It would be useful if we could estimate how
this number typically varies with the macroscopic parameters of the system.
The easiest way to do this is to consider a specific example. For instance,
an ideal gas made up of spinless monatomic particles. This is a particularly
simple example,
because, for such a gas, the particles possess translational, but no
internal (e.g., vibrational, rotational, or spin), degrees of freedom.
By definition, interatomic forces are negligible in an ideal gas. In other
words, the individual particles
move in an approximately uniform potential.
It follows that the energy of the gas is just
the total translational kinetic energy of its constituent particles. In other words,
be the total number of microscopic states that
satisfy these constraints.
It would be useful if we could estimate how
this number typically varies with the macroscopic parameters of the system.
The easiest way to do this is to consider a specific example. For instance,
an ideal gas made up of spinless monatomic particles. This is a particularly
simple example,
because, for such a gas, the particles possess translational, but no
internal (e.g., vibrational, rotational, or spin), degrees of freedom.
By definition, interatomic forces are negligible in an ideal gas. In other
words, the individual particles
move in an approximately uniform potential.
It follows that the energy of the gas is just
the total translational kinetic energy of its constituent particles. In other words,
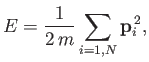 |
(3.20) |
where 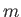 is the particle mass,
is the particle mass, 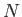 the total number of particles,
and
the total number of particles,
and 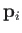 the
vector momentum of the
the
vector momentum of the 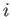 th particle.
th particle.
Consider the system in the
limit in which the energy, 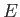 , of the gas is
much greater than the ground-state energy, so that all of the
quantum numbers are large.
The classical version of statistical mechanics, in which we
divide up phase-space into cells of equal volume, is valid in this limit.
The number of
states,
, of the gas is
much greater than the ground-state energy, so that all of the
quantum numbers are large.
The classical version of statistical mechanics, in which we
divide up phase-space into cells of equal volume, is valid in this limit.
The number of
states,
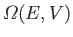 , lying between the energies
, lying between the energies 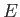 and
and
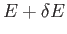 is simply
equal to the number of cells in phase-space contained between these energies.
In other words,
is simply
equal to the number of cells in phase-space contained between these energies.
In other words,
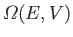 is proportional to the volume of
phase-space between these two energies:
is proportional to the volume of
phase-space between these two energies:
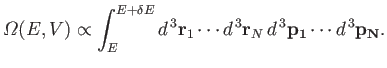 |
(3.21) |
Here, the integrand is the element of volume of phase-space, with
where 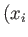 ,
, 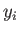 ,
, 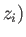 and
and 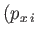 ,
, 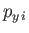 ,
, 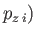 are the Cartesian coordinates and momentum components of the
are the Cartesian coordinates and momentum components of the 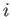 th particle,
respectively.
The integration is over all coordinates and momenta such that the total energy
of the system lies between
th particle,
respectively.
The integration is over all coordinates and momenta such that the total energy
of the system lies between 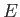 and
and
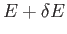 .
.
For an ideal gas, the total energy 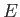 does not depend on the positions of the
particles. [See Equation (3.20).] This implies that the integration over the
position vectors,
does not depend on the positions of the
particles. [See Equation (3.20).] This implies that the integration over the
position vectors, 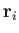 ,
can be performed immediately. Because each integral over
,
can be performed immediately. Because each integral over 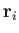 extends over
the volume of the container (the particles are, of course, not allowed to stray
outside the container),
extends over
the volume of the container (the particles are, of course, not allowed to stray
outside the container),
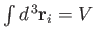 . There
are
. There
are 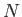 such integrals, so Equation (3.21) reduces to
such integrals, so Equation (3.21) reduces to
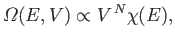 |
(3.24) |
where
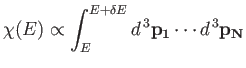 |
(3.25) |
is a momentum-space integral that is independent of the volume.
The energy of the system can be written
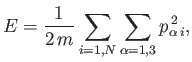 |
(3.26) |
because
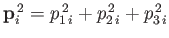 ,
denoting the
,
denoting the  ,
, 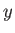 ,
,
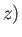 components by (1, 2, 3), respectively. The previous sum contains
components by (1, 2, 3), respectively. The previous sum contains 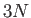 square terms.
For
square terms.
For 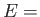 constant, Equation (3.26) describes the locus of a
sphere of radius
constant, Equation (3.26) describes the locus of a
sphere of radius
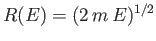 in
the
in
the 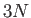 -dimensional space of the momentum components. Hence,
-dimensional space of the momentum components. Hence, 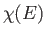 is
proportional to the volume of momentum phase-space contained in the region lying between the sphere of radius
is
proportional to the volume of momentum phase-space contained in the region lying between the sphere of radius 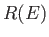 , and that of slightly larger
radius
, and that of slightly larger
radius
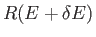 . This volume is
proportional to the area of the inner sphere multiplied by
. This volume is
proportional to the area of the inner sphere multiplied by
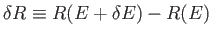 .
Because the area varies like
.
Because the area varies like
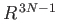 , and
, and
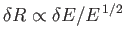 ,
we have
,
we have
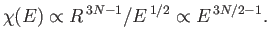 |
(3.27) |
Combining this result with
Equation (3.24), we obtain
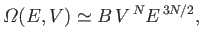 |
(3.28) |
where 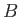 is a constant independent of
is a constant independent of 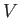 or
or 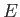 , and we have also
made use of the fact that
, and we have also
made use of the fact that 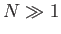 . Note that, because the number of degrees of freedom of the
system is
. Note that, because the number of degrees of freedom of the
system is 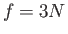 , the previous relation can be very approximately written
, the previous relation can be very approximately written
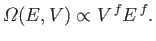 |
(3.29) |
In other words, the density of states varies like the extensive
macroscopic parameters of the system
raised to the power of the number of degrees of freedom. An extensive parameter is
one that scales with the size of the system (e.g., the volume). (See Section 7.8.)
Because thermodynamic
systems generally possess a very large number of degrees of freedom, this
result implies that the density of states
is an exceptionally rapidly increasing function of
the energy and volume.
This result, which turns out to be quite general, is of great significance in statistical
thermodynamics.


Next: Exercises
Up: Statistical Mechanics
Previous: Probability Calculations
Richard Fitzpatrick
2016-01-25
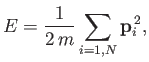
![]() , of the gas is
much greater than the ground-state energy, so that all of the
quantum numbers are large.
The classical version of statistical mechanics, in which we
divide up phase-space into cells of equal volume, is valid in this limit.
The number of
states,
, of the gas is
much greater than the ground-state energy, so that all of the
quantum numbers are large.
The classical version of statistical mechanics, in which we
divide up phase-space into cells of equal volume, is valid in this limit.
The number of
states,
![]() , lying between the energies
, lying between the energies ![]() and
and
![]() is simply
equal to the number of cells in phase-space contained between these energies.
In other words,
is simply
equal to the number of cells in phase-space contained between these energies.
In other words,
![]() is proportional to the volume of
phase-space between these two energies:
is proportional to the volume of
phase-space between these two energies:
![]() does not depend on the positions of the
particles. [See Equation (3.20).] This implies that the integration over the
position vectors,
does not depend on the positions of the
particles. [See Equation (3.20).] This implies that the integration over the
position vectors, ![]() ,
can be performed immediately. Because each integral over
,
can be performed immediately. Because each integral over ![]() extends over
the volume of the container (the particles are, of course, not allowed to stray
outside the container),
extends over
the volume of the container (the particles are, of course, not allowed to stray
outside the container),
![]() . There
are
. There
are ![]() such integrals, so Equation (3.21) reduces to
such integrals, so Equation (3.21) reduces to