Next: Constant- Linear Resonant Response Up: Linear Resonant Response Model Previous: Fourier Transformation Contents
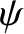 Limit
Limit
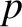 space. In the small-
space. In the small-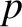 layer, suppose that Equation (5.78) reduces to
layer, suppose that Equation (5.78) reduces to
![$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dp}\!\left[\frac{p^2}{-{\rm i}\,(Q-Q_E-Q_e) + p^2}\,\frac{dY_e}{dp}\right]\simeq 0$](img2161.png) |
(5.84) |
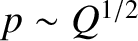 . Integrating directly, we find that
for
. Integrating directly, we find that
for
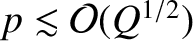 , where use has been made of Equation (5.83). The two-layer approximation is
equivalent to the well-known constant-
, where use has been made of Equation (5.83). The two-layer approximation is
equivalent to the well-known constant-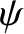 approximation [17].
approximation [17].
In the large-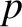 layer, for
layer, for
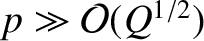 , we obtain
, we obtain
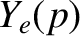 bounded as
bounded as
 . Asymptotic matching to the small-
. Asymptotic matching to the small-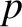 layer solution (5.85) yields the boundary
condition
as
layer solution (5.85) yields the boundary
condition
as
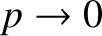 .
.
In the various constant-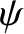 linear response regimes considered in Section 5.9, Equation (5.86) reduces to an
equation of the form
linear response regimes considered in Section 5.9, Equation (5.86) reduces to an
equation of the form
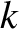 is real and non-negative, and
is real and non-negative, and 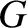 is a complex constant. Let
is a complex constant. Let
 and
and
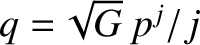 , where
, where
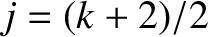 . The previous equation transforms into a modified Bessel equation of general order,
. The previous equation transforms into a modified Bessel equation of general order,
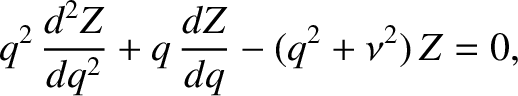 |
(5.89) |
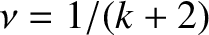 . The solution that is bounded as
. The solution that is bounded as
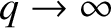 has the small-
has the small-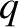 expansion [1]
where
expansion [1]
where
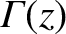 is a gamma function.
A comparison of this expression with Equation (5.87) reveals that
is a gamma function.
A comparison of this expression with Equation (5.87) reveals that
![$\displaystyle \skew{6}\hat{\mit\Delta} = \frac{\nu^{2\nu-1}\,\pi\,{\mit\Gamma}(...
...u)}{{\mit\Gamma}(\nu)}\left[-{\rm i}\,\left(Q-Q_E-\,Q_e\right)\right]G^{\,\nu}.$](img2180.png) |
(5.91) |
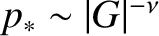 , where
, where 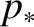 denotes the width of the large-
denotes the width of the large-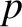 layer in
layer in 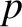 space. This width must be larger than
space. This width must be larger than 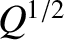 (i.e., the width of the small-
(i.e., the width of the small-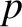 layer) in order for the constant-
layer) in order for the constant-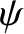 approximation to hold. Finally, it is easily demonstrated that the neglect of the term involving
approximation to hold. Finally, it is easily demonstrated that the neglect of the term involving 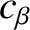 in Equation (5.74) is
justified provided that
in Equation (5.74) is
justified provided that
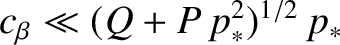 .
.