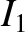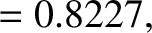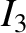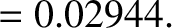Evaluation of Integrals
Figure: 8.1
The integrands
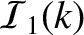 ,
,
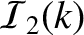 , and
, and
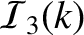 .
.
|
|
In order to evaluate the integrals (8.109)–(8.111), it is helpful to define the new magnetic flux-surface label
![$k=[(1+{\mit\Omega})/2]^{1/2}$](img2907.png) .
It follows from Equation (8.55) that
.
It follows from Equation (8.55) that 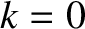 at the O-points of the magnetic island chain, and
at the O-points of the magnetic island chain, and 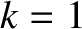 on the magnetic separatrix.
It is easily demonstrated that
on the magnetic separatrix.
It is easily demonstrated that
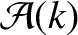 |
![\begin{align*}\equiv 2\,k\,\langle 1\rangle=\frac{2}{\pi}\left\{
\begin{array}{llr} k\,K(k)&~~~~&0\leq k\leq 1\\ [0.5ex]
K(1/k)&&k>1\end{array}\right.,\end{align*}](img2910.png) |
(8.112) |
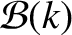 |
![\begin{align*}\equiv \langle \vert X\vert\rangle=\left\{
\begin{array}{llr} (2/\...
...,\sin^{-1}(k)&~~~~&0\leq k\leq 1\\ [0.5ex]
1&&k>1\end{array}\right.,\end{align*}](img2912.png) |
(8.113) |
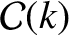 |
![\begin{align*}\equiv \frac{\langle X^2\rangle}{2\,k}=\frac{2}{\pi}\left\{
\begin...
...,K(k)]/k&~~~~&0\leq k\leq 1\\ [0.5ex]
E(1/k)&&k>1\end{array}\right.,\end{align*}](img2914.png) |
(8.114) |
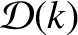 |
![\begin{align*}\equiv \frac{\langle \vert X\vert^3\rangle}{4\,k^2}=\left\{
\begin...
...)]&~~~~&0\leq k\leq 1\\ [0.5ex]
1-1/(2\,k^2)&&k>1\end{array}\right.,\end{align*}](img2916.png) |
(8.115) |
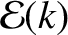 |
![\begin{align*}\equiv \frac{\langle X^4\rangle}{8\,k^3}=\frac{2}{3\pi}\left\{
\be...
...]
[2\,(2-1/k^2)\,E(1/k) - (1-1/k^2)\,K(1/k)]&&k>1\end{array}\right.,\end{align*}](img2918.png) |
(8.116) |
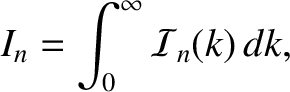 |
(8.119) |
for 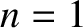 ,
, 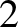 ,
, 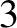 , where
, where
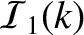 |
![$\displaystyle = \frac{4\left[(2\,k^2-1)\,{\cal A} - 2\,k^2\,{\cal C}\right]^2}{{\cal A}},$](img2927.png) |
(8.120) |
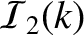 |
![$\displaystyle = \left\{\begin{array}{llr} 0 &~~~~& 0\leq k < 1\\ [0.5ex]
(1-k\,...
...cal C}/({\cal A}\,{\cal E})\right]/{\cal F}(\infty)&&k\geq 1\end{array}\right.,$](img2929.png) |
(8.121) |
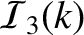 |
![$\displaystyle = \left\{\begin{array}{llr} 0 &~~~~& 0\leq k < 1\\ [0.5ex]
k\,{\c...
...C}^2/({\cal A}\,{\cal E})\right]/{\cal F}^2(\infty)&&k\geq 1\end{array}\right.,$](img2931.png) |
(8.122) |
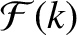 |
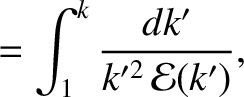 |
(8.123) |
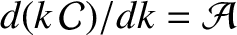 .
.
The integrands
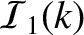 ,
,
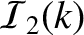 , and
, and
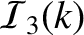 are shown in Figure 8.1.
Note that
are shown in Figure 8.1.
Note that
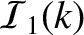 has a logarithmic (and, therefore, integrable) singularity at the island separatrix (
has a logarithmic (and, therefore, integrable) singularity at the island separatrix (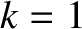 ).
The values of the integrals themselves are
).
The values of the integrals themselves are
![$k=[(1+{\mit\Omega})/2]^{1/2}$](img2907.png) .
It follows from Equation (8.55) that
.
It follows from Equation (8.55) that 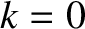 at the O-points of the magnetic island chain, and
at the O-points of the magnetic island chain, and 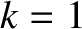 on the magnetic separatrix.
It is easily demonstrated that
on the magnetic separatrix.
It is easily demonstrated that
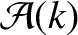
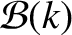
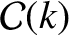
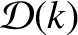
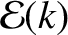
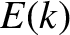
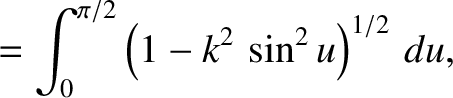
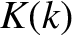
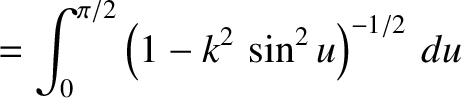
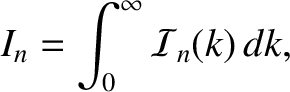
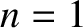 ,
, 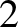 ,
, 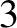 , where
, where
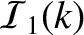
![$\displaystyle = \frac{4\left[(2\,k^2-1)\,{\cal A} - 2\,k^2\,{\cal C}\right]^2}{{\cal A}},$](img2927.png)
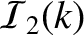
![$\displaystyle = \left\{\begin{array}{llr} 0 &~~~~& 0\leq k < 1\\ [0.5ex]
(1-k\,...
...cal C}/({\cal A}\,{\cal E})\right]/{\cal F}(\infty)&&k\geq 1\end{array}\right.,$](img2929.png)
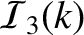
![$\displaystyle = \left\{\begin{array}{llr} 0 &~~~~& 0\leq k < 1\\ [0.5ex]
k\,{\c...
...C}^2/({\cal A}\,{\cal E})\right]/{\cal F}^2(\infty)&&k\geq 1\end{array}\right.,$](img2931.png)
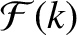
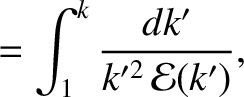
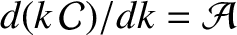 .
.
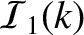 ,
,
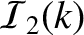 , and
, and
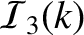 are shown in Figure 8.1.
Note that
are shown in Figure 8.1.
Note that
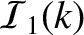 has a logarithmic (and, therefore, integrable) singularity at the island separatrix (
has a logarithmic (and, therefore, integrable) singularity at the island separatrix (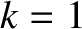 ).
The values of the integrals themselves are
).
The values of the integrals themselves are