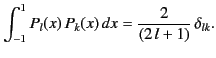

Next: Spherical Harmonics
Up: Potential Theory
Previous: Introduction
Associated Legendre Functions
The associated Legendre functions,
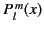 , are the well-behaved solutions of the
differential equation
, are the well-behaved solutions of the
differential equation
![$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\!\left[(1-x^{\,2})\,\frac{dP_l^{\,m}}{dx}\right]+\left[l\,(l+1)-\frac{m^{\,2}}{1-x^{\,2}}\right]P_l^{\,m} = 0,$](img673.png) |
(292) |
for 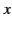 in the range
in the range
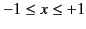 .
Here,
.
Here, 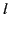 is a non-negative integer (known as the degree), and
is a non-negative integer (known as the degree), and 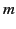 is an integer (known as the order) lying in the range
is an integer (known as the order) lying in the range
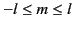 .
The functions themselves take the form
.
The functions themselves take the form![[*]](footnote.png)
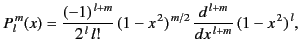 |
(293) |
which implies that
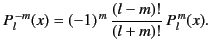 |
(294) |
Assuming that
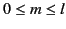 , the
, the
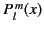 satisfy the orthogonality condition
satisfy the orthogonality condition
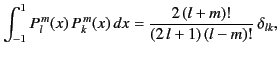 |
(295) |
where
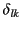 is a Kronecker delta symbol.
is a Kronecker delta symbol.
The associated Legendre functions of order 0 (i.e., 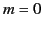 ) are called Legendre polynomials, and
are denoted the
) are called Legendre polynomials, and
are denoted the 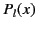 : that is,
: that is,
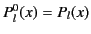 . It follows that
. It follows that![[*]](footnote.png)
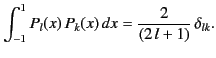 |
(296) |
It can also be shown that
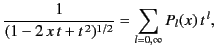 |
(297) |
provided 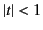 and
and 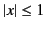 .
.
All of the associated Legendre functions of degree less than 3 are listed below:
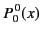 |
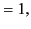 |
(298) |
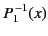 |
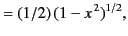 |
(299) |
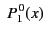 |
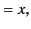 |
(300) |
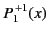 |
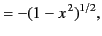 |
(301) |
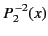 |
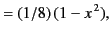 |
(302) |
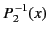 |
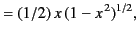 |
(303) |
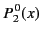 |
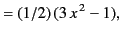 |
(304) |
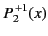 |
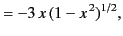 |
(305) |
 |
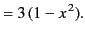 |
(306) |

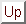

Next: Spherical Harmonics
Up: Potential Theory
Previous: Introduction
Richard Fitzpatrick
2014-06-27
![$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\!\left[(1-x^{\,2})\,\frac{dP_l^{\,m}}{dx}\right]+\left[l\,(l+1)-\frac{m^{\,2}}{1-x^{\,2}}\right]P_l^{\,m} = 0,$](img673.png)
![$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\!\left[(1-x^{\,2})\,\frac{dP_l^{\,m}}{dx}\right]+\left[l\,(l+1)-\frac{m^{\,2}}{1-x^{\,2}}\right]P_l^{\,m} = 0,$](img673.png)
![[*]](footnote.png)
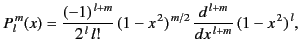
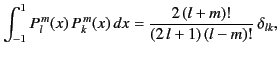
![]() ) are called Legendre polynomials, and
are denoted the
) are called Legendre polynomials, and
are denoted the ![]() : that is,
: that is,
![]() . It follows that
. It follows that![[*]](footnote.png)