

Next: Worked example 10.4: Truck
Up: Statics
Previous: Worked example 10.2: Rod
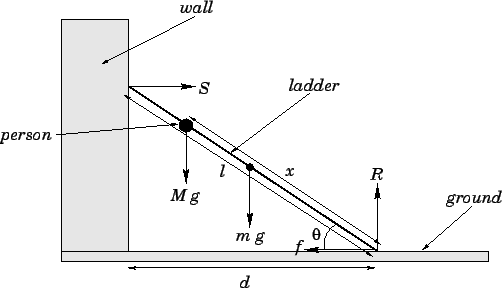
Question: A uniform ladder of mass
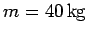 and length
and length
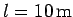 is leaned against a smooth vertical wall. A person
of mass
is leaned against a smooth vertical wall. A person
of mass
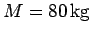 stands on the ladder a distance
stands on the ladder a distance 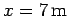 from the bottom, as measured along the ladder. The foot of the ladder
is
from the bottom, as measured along the ladder. The foot of the ladder
is
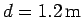 from the bottom of the wall. What is the force exerted by the
wall on the ladder? What is the normal force exerted by the floor on the ladder?
from the bottom of the wall. What is the force exerted by the
wall on the ladder? What is the normal force exerted by the floor on the ladder?
Answer: The angle 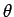 subtended by the ladder with the ground
satisfies
subtended by the ladder with the ground
satisfies
Let 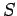 be the normal reaction at the wall, let
be the normal reaction at the wall, let 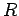 be the normal reaction at the ground,
and let
be the normal reaction at the ground,
and let 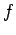 be the frictional force exerted by the ground on the ladder, as shown
in the diagram. Consider the torque acting on the ladder about the point where
it meets the ground. Only three forces contribute to this torque: the weight,
be the frictional force exerted by the ground on the ladder, as shown
in the diagram. Consider the torque acting on the ladder about the point where
it meets the ground. Only three forces contribute to this torque: the weight, 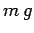 , of
the ladder, which acts half-way along the ladder; the weight,
, of
the ladder, which acts half-way along the ladder; the weight, 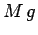 , of the person,
which acts a distance
, of the person,
which acts a distance 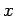 along the ladder; and the reaction,
along the ladder; and the reaction, 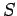 , at the wall, which acts
at the top of the ladder. The lever arms associated with these three forces are
, at the wall, which acts
at the top of the ladder. The lever arms associated with these three forces are
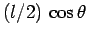 ,
, 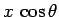 , and
, and 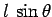 , respectively.
Note that the reaction force acts to twist the ladder in the opposite sense to
the two weights. Hence, setting the net torque to zero, we obtain
, respectively.
Note that the reaction force acts to twist the ladder in the opposite sense to
the two weights. Hence, setting the net torque to zero, we obtain
which yields
The condition that zero net vertical force acts on the ladder yields
Hence,


Next: Worked example 10.4: Truck
Up: Statics
Previous: Worked example 10.2: Rod
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-02-02

![]() subtended by the ladder with the ground
satisfies
subtended by the ladder with the ground
satisfies