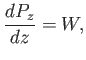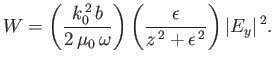

Next: Collisional Damping
Up: Wave Propagation Through Inhomogeneous
Previous: Resonances
Resonant Layers
Consider the situation, studied in the
previous section, in which a plane wave, polarized in the 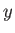 -direction,
is launched along the
-direction,
is launched along the  -axis, from an antenna located at large positive
-axis, from an antenna located at large positive  ,
and absorbed at a resonance located at
,
and absorbed at a resonance located at  . In the vicinity
of the resonant point, the electric component of the wave satisfies
. In the vicinity
of the resonant point, the electric component of the wave satisfies
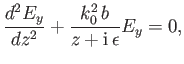 |
(6.55) |
where 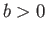 and
and
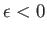 .
.
The time-averaged Poynting flux in the 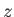 -direction is written
-direction is written
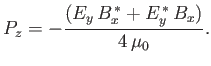 |
(6.56) |
Now, the Faraday-Maxwell equation yields
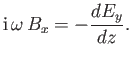 |
(6.57) |
Thus, we have
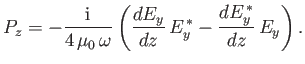 |
(6.58) |
Let us ascribe any variation of 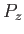 with
with 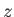 to the wave energy emitted by the
plasma. We then obtain
to the wave energy emitted by the
plasma. We then obtain
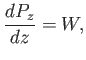 |
(6.59) |
where 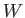 is the power emitted by the plasma per unit volume.
It follows that
is the power emitted by the plasma per unit volume.
It follows that
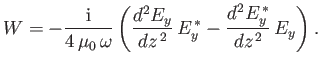 |
(6.60) |
Equations (6.55) and (6.60) yield
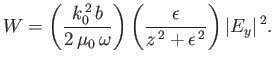 |
(6.61) |
Note that 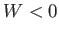 , because
, because
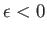 , so wave energy is absorbed by the
plasma. It is clear, from the previous formula, that the absorption takes
place in a narrow layer, of thickness
, so wave energy is absorbed by the
plasma. It is clear, from the previous formula, that the absorption takes
place in a narrow layer, of thickness
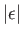 , centered on the
resonance point,
, centered on the
resonance point,  .
.


Next: Collisional Damping
Up: Wave Propagation Through Inhomogeneous
Previous: Resonances
Richard Fitzpatrick
2016-01-23
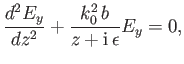
![]() -direction is written
-direction is written
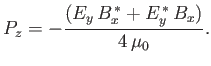
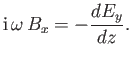
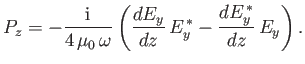
![]() with
with ![]() to the wave energy emitted by the
plasma. We then obtain
to the wave energy emitted by the
plasma. We then obtain