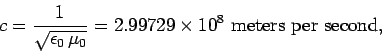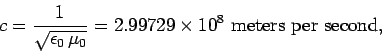

Next: The Lorentz transformation
Up: Relativity and electromagnetism
Previous: Introduction
Physical phenomena are conventionally described relative to some
frame of reference which allows us to define
fundamental quantities such
as position and time. Of course,
there are very many different ways
of choosing a reference frame, but it is generally convenient to
restrict our choice to the set of rigid inertial frames.
A classical rigid reference frame is the imagined extension of
a rigid body. For instance, the Earth determines a rigid frame
throughout all space, consisting of all those points which
remain rigidly at rest relative to the Earth, and to each other.
We can associate an orthogonal Cartesian coordinate system  with
such a frame, by choosing three mutually orthogonal planes within it,
and measuring
with
such a frame, by choosing three mutually orthogonal planes within it,
and measuring 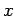 ,
, 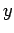 , and
, and 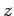 as perpendicular distances from these planes. A time
coordinate must also be defined, in order that the system can be used to
specify events. A rigid frame, endowed with such properties, is called
a Cartesian frame. The description given above presupposes that the
underlying
geometry of space is Euclidian, which is reasonable provided that
gravitational effects are negligible (we shall assume that this is the case).
An inertial frame is a Cartesian frame in which free particles
move without acceleration, in accordance with Newton's first law of motion.
There are an infinite number of different inertial frames, moving with
some
constant velocity with respect to one another.
as perpendicular distances from these planes. A time
coordinate must also be defined, in order that the system can be used to
specify events. A rigid frame, endowed with such properties, is called
a Cartesian frame. The description given above presupposes that the
underlying
geometry of space is Euclidian, which is reasonable provided that
gravitational effects are negligible (we shall assume that this is the case).
An inertial frame is a Cartesian frame in which free particles
move without acceleration, in accordance with Newton's first law of motion.
There are an infinite number of different inertial frames, moving with
some
constant velocity with respect to one another.
The key to understanding
special relativity is Einstein's relativity principle,
which states that:
All inertial frames are totally equivalent for the performance
of all physical experiments.
In other words, it is impossible to perform a physical experiment which
differentiates in any fundamental sense
between different inertial frames. By definition, Newton's laws
of motion take the same form in all inertial frames. Einstein
generalized this result in his special theory of relativity by
asserting that all
laws of physics take the same form in all inertial frames.
Consider a wave-like disturbance.
In general, such a disturbance propagates at a fixed velocity
with respect to the medium in which the disturbance takes place.
For instance, sound waves (at S.T.P.) propagate at 343 meters per
second with respect to air. So, in the inertial frame in which
air is stationary, sound waves appear to propagate at
343 meters per second.
Sound waves appear to propagate at a different velocity any
inertial frame which is moving
with respect to the air.
However, this does not violate the relativity principle, since if the air
were stationary in the second frame then sound waves would appear to
propagate at 343 meters per second in this frame as well. In other words,
exactly the same experiment (e.g.,
the determination of the speed of sound relative to
stationary air)
performed in two different inertial frames
of reference yields exactly the same result, in accordance with the relativity
principle.
Consider, now, a wave-like disturbance which is self-regenerating, and
does not require a medium through which to propagate. The most well-known
example of such a disturbance is a light wave. Another example is
a gravity wave. According to electromagnetic theory, the speed of propagation
of a light wave through a vacuum is
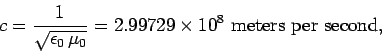 |
(1323) |
where 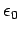 and
and 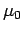 are physical constants which can
be evaluated by performing two simple experiments which
involve measuring the
force of attraction between two fixed changes and two fixed parallel
current carrying wires. According to the relativity principle, these
experiments must yield the same values for
are physical constants which can
be evaluated by performing two simple experiments which
involve measuring the
force of attraction between two fixed changes and two fixed parallel
current carrying wires. According to the relativity principle, these
experiments must yield the same values for 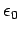 and
and 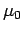 in all
inertial frames. Thus, the speed of light must be the same in all
inertial frames. In fact, any disturbance which does not require
a medium to propagate through must appear to travel at the same velocity in
all inertial frames, otherwise we could differentiate inertial frames
using the apparent propagation speed of the disturbance, which
would violate the
relativity principle.
in all
inertial frames. Thus, the speed of light must be the same in all
inertial frames. In fact, any disturbance which does not require
a medium to propagate through must appear to travel at the same velocity in
all inertial frames, otherwise we could differentiate inertial frames
using the apparent propagation speed of the disturbance, which
would violate the
relativity principle.


Next: The Lorentz transformation
Up: Relativity and electromagnetism
Previous: Introduction
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-02-02