Next: Secular perturbation theory Up: Three-body problem Previous: Stability of Lagrange points
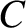 , which is defined in Equation (9.10), is a constant of the motion in the circular
restricted three-body problem.
, which is defined in Equation (9.10), is a constant of the motion in the circular
restricted three-body problem.
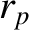 and inclination
and inclination 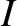 (with respect to Jupiter's orbital plane) is
disturbed by a close encounter with Jupiter such that its orbit is converted into an
ellipse of major radius
(with respect to Jupiter's orbital plane) is
disturbed by a close encounter with Jupiter such that its orbit is converted into an
ellipse of major radius 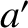 , eccentricity
, eccentricity 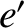 , and inclination
, and inclination 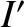 . Demonstrate that
. Demonstrate that
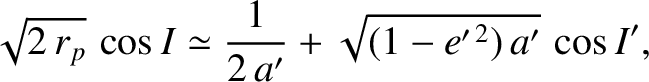
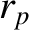 and inclination
and inclination 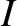 (with respect to Jupiter's orbital plane), whose
asymptotes subtend an acute angle
(with respect to Jupiter's orbital plane), whose
asymptotes subtend an acute angle 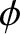 with respect to one another, is
disturbed by a close encounter with Jupiter such that its orbit is converted into an
ellipse of major radius
with respect to one another, is
disturbed by a close encounter with Jupiter such that its orbit is converted into an
ellipse of major radius 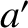 , eccentricity
, eccentricity 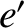 , and inclination
, and inclination 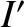 . Demonstrate that
. Demonstrate that
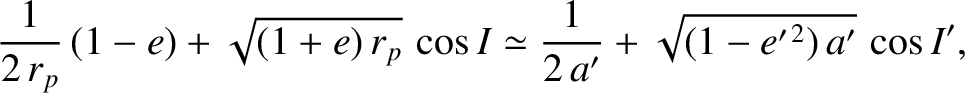
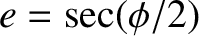 , and all lengths are normalized to the major radius of Jupiter.
, and all lengths are normalized to the major radius of Jupiter.
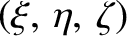 be the coordinates of mass
be the coordinates of mass 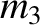 in the inertial frame, and
let
in the inertial frame, and
let
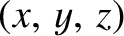 be the corresponding coordinates in the co-rotating frame. It
follows that
be the corresponding coordinates in the co-rotating frame. It
follows that
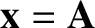
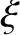
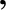
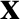 is the column vector of the co-rotating coordinates,
is the column vector of the co-rotating coordinates,
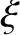 is the column vector of the inertial coordinates,
and
is the column vector of the inertial coordinates,
and
![$\displaystyle {\bf A} = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} \cos \omega t, & \sin \omega t,&0\\ [0.5ex]
-\sin\omega t,&\cos\omega t,&0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&0,&1\end{array}\right).
$](img2318.png)
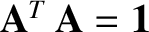 , where
, where 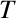 denotes a transpose, and
denotes a transpose, and
![$\displaystyle {\bf 1} = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} 1, & 0, &0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&1,&0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&0,&1\end{array}\right).
$](img2320.png)
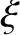 , or
, or
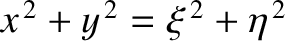 .
.
Show that
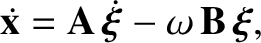
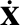 is the column vector of the time derivatives of the co-rotating coordinates,
is the column vector of the time derivatives of the co-rotating coordinates,
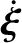 is the column vector of the time derivatives of the inertial coordinates, and
is the column vector of the time derivatives of the inertial coordinates, and
![$\displaystyle {\bf B} = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} \sin \omega t, & -\cos \omega t&0\\ [0.5ex]
\cos\omega t,&\sin\omega t&0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&0,&0\end{array}\right).
$](img2327.png)
Demonstrate that
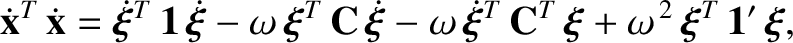
![$\displaystyle {\bf 1}' = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} 1, & 0, &0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&1,&0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&0,&0\end{array}\right),
$](img2329.png)
![$\displaystyle {\bf C} = \left(\begin{array}{ccc} 0,& 1, &0\\ [0.5ex]
-1,&0,&0\\ [0.5ex]
0,&0,&0\end{array}\right).
$](img2330.png)
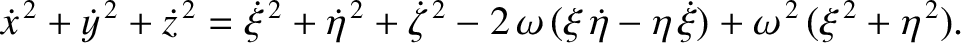
Finally, show that the Jacobi constant in the co-rotating frame,
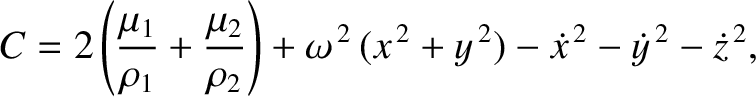
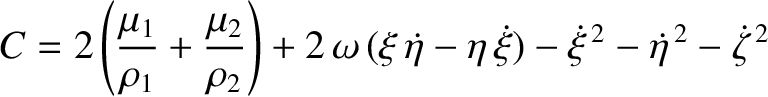
 -
- plane of the co-rotating frame is
plane of the co-rotating frame is
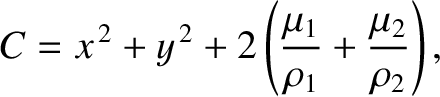
 is the value of the Jacobi constant, and
is the value of the Jacobi constant, and
![$\rho_1=[(x+\mu_2)^2+y^{\,2}]^{1/2}$](img2335.png) and
and
![$\rho_2=[(x-\mu_1)^2+y^{\,2}]^{1/2}$](img2336.png) are the distances to the primary and secondary masses, respectively. The critical zero-velocity curve that passes
through the
are the distances to the primary and secondary masses, respectively. The critical zero-velocity curve that passes
through the 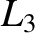 point, when
point, when
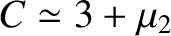 , has two branches. Defining polar coordinates such that
, has two branches. Defining polar coordinates such that
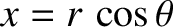 and
and
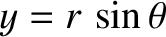 , show that when
, show that when
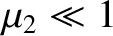 the branches intersect the unit circle
the branches intersect the unit circle 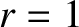 at
at
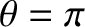 and
and
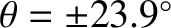 . (Modified from Murray and Dermott 1999.)
. (Modified from Murray and Dermott 1999.)
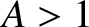 , where
, where
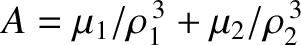 . Here,
. Here, 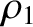 and
and 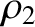 are the distances to
the masses
are the distances to
the masses 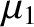 and
and 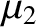 , respectively. Let
, respectively. Let
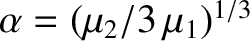 and
and
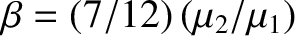 . Consider the limit
. Consider the limit
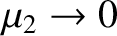 .
Show that
close to
.
Show that
close to 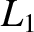 , where
, where
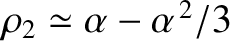 and
and
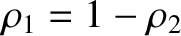 , the parameter
, the parameter  takes the value
takes the value
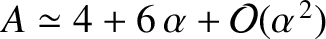 . Likewise, show that close to
. Likewise, show that close to  , where
, where
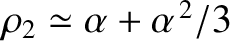 and
and
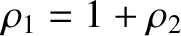 ,
the parameter
,
the parameter  takes the value
takes the value
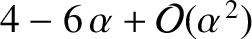 . Finally, show that close to
. Finally, show that close to 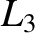 , where
, where
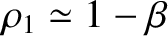 and
and
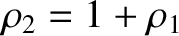 , the parameter
, the parameter  takes the value
takes the value
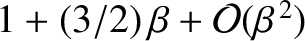 . Hence, deduce that the three co-linear Lagrange
points are all linearly unstable. Demonstrate that, in the case of the
. Hence, deduce that the three co-linear Lagrange
points are all linearly unstable. Demonstrate that, in the case of the 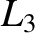 point,
the growth-rate of the fastest growing instability is
point,
the growth-rate of the fastest growing instability is
![$\gamma\simeq \left[\sqrt{(21/8)\,\mu_2} + {\cal O}(\mu_2)\right]\omega $](img2354.png) . (Modified from Murray and Dermott 1999.)
. (Modified from Murray and Dermott 1999.)
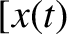 ,
, 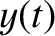 ,
, ![$z(t)]$](img2357.png) is a valid trajectory for
is a valid trajectory for 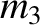 in the co-rotating frame then
in the co-rotating frame then
![$[x(t),\,y(t),\,-z(t)]$](img2358.png) and
and 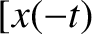 ,
, 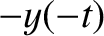 ,
, ![$z(-t)]$](img2361.png) are also valid trajectories. Show that
if
are also valid trajectories. Show that
if
![$[x(t),\,y(t),\,z(t)]$](img2362.png) is a valid trajectory when
is a valid trajectory when
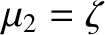 (where
(where
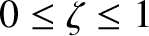 ) then
) then
![$[-x(t),\,-y(t),\,z(t)]$](img2365.png) is a valid trajectory
when
is a valid trajectory
when
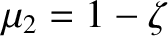 .
.
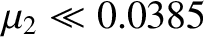 , so that the
, so that the 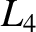 and
and 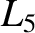 points are stable equilibrium points (in the co-rotating frame) for the tertiary mass. Consider motion (in the co-rotating frame) of the tertiary mass in the vicinity of
points are stable equilibrium points (in the co-rotating frame) for the tertiary mass. Consider motion (in the co-rotating frame) of the tertiary mass in the vicinity of 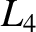 that
is confined to the
that
is confined to the 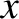 -
-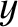 plane.
Let
plane.
Let
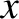 |
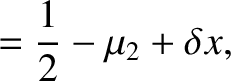 |
|
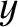 |
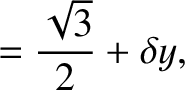 |
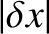 ,
,
 . It is helpful to rotate the Cartesian axes through
. It is helpful to rotate the Cartesian axes through 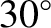 , so that
, so that
![$\displaystyle \left(\begin{array}{c}\delta x\\ [0.5ex]\delta y\end{array}\right...
...}\right)
\left(\begin{array}{c}\delta x'\\ [0.5ex]\delta y'\end{array}\right).
$](img2373.png)
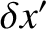 parameterizes displacements from
parameterizes displacements from 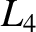 that are tangential to the unit circle on which the mass
that are tangential to the unit circle on which the mass 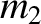 ,
and the
,
and the 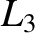 ,
, 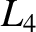 , and
, and 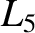 points,
lie, whereas
points,
lie, whereas 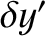 parameterizes radial displacements. Writing
parameterizes radial displacements. Writing
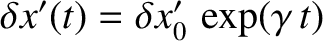 and
and
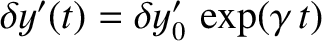 , where
, where
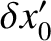 ,
,
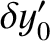 ,
, 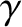 are constants,
demonstrate that
are constants,
demonstrate that
![$\displaystyle \left(\begin{array}{cc}\sqrt{3}\,\gamma^{\,2}/2+\gamma - 3\sqrt{3...
...a y_0'\end{array}\right)=\left(\begin{array}{c}0\\ [0.5ex]0\end{array}\right),
$](img2380.png)
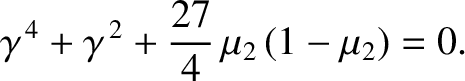
Show that the general solution to the preceding dispersion relation is a linear combination of two normal modes of oscillation, and that the higher frequency mode takes the form
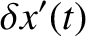 |
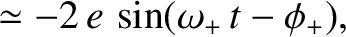 |
|
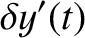 |
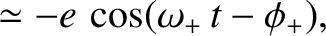 |
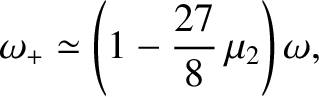
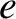 ,
, 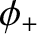 are arbitrary constants. Demonstrate that, in the
original inertial reference frame, the addition of the preceding normal mode to the unperturbed orbit of the tertiary mass (in the limit
are arbitrary constants. Demonstrate that, in the
original inertial reference frame, the addition of the preceding normal mode to the unperturbed orbit of the tertiary mass (in the limit 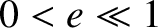 ) converts
a circular orbit into a Keplerian ellipse of eccentricity
) converts
a circular orbit into a Keplerian ellipse of eccentricity 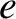 . In addition, show that the perihelion point of the new orbit precesses (in the direction of the orbital motion)
at the rate
. In addition, show that the perihelion point of the new orbit precesses (in the direction of the orbital motion)
at the rate
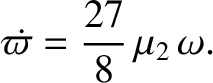
Demonstrate that (in the co-rotating reference frame) the second normal mode takes the form
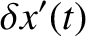 |
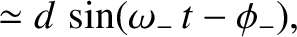 |
|
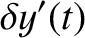 |
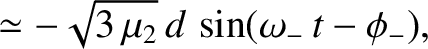 |
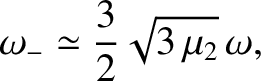
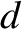 ,
, 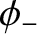 are arbitrary constants. This type of motion, which entails relatively small amplitude radial oscillations, combined with
much larger amplitude tangential oscillations, is known as libration.
are arbitrary constants. This type of motion, which entails relatively small amplitude radial oscillations, combined with
much larger amplitude tangential oscillations, is known as libration.
Finally, consider a Trojan asteroid trapped in the vicinity of the 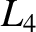 point of the Sun-Jupiter system. Demonstrate
that the libration period of the asteroid (in the co-rotating frame) is approximately
point of the Sun-Jupiter system. Demonstrate
that the libration period of the asteroid (in the co-rotating frame) is approximately 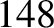 years, whereas its perihelion precession period
(in the inertial frame) is approximately
years, whereas its perihelion precession period
(in the inertial frame) is approximately 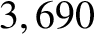 years. Show that, in the co-rotating frame, the libration orbit is
an ellipse that is elongated in the direction of the tangent to the Jovian orbit in the ratio
years. Show that, in the co-rotating frame, the libration orbit is
an ellipse that is elongated in the direction of the tangent to the Jovian orbit in the ratio 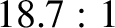 .
.