Next: Gauss's Law Up: Newtonian Gravity Previous: Newtonian Gravity
Consider a system consisting of two point mass objects. Let object 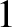 have mass
have mass 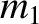 and displacement
and displacement 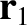 .
Let object
.
Let object 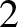 have mass
have mass 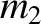 and displacement
and displacement 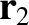 .
The gravitational force exerted on object 2 by object 1 is
written
.
The gravitational force exerted on object 2 by object 1 is
written
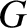 , is called the universal gravitational constant,
and takes the value
This constant was first `measured' by Henry Cavendish in 1798 (to be more exact, the result
, is called the universal gravitational constant,
and takes the value
This constant was first `measured' by Henry Cavendish in 1798 (to be more exact, the result
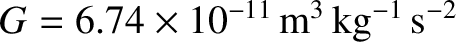 can be inferred from Cavendish's results).
An equal and opposite force to (1.238) acts on object 1.
can be inferred from Cavendish's results).
An equal and opposite force to (1.238) acts on object 1.
Suppose that we have a system of 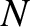 point mass objects. Let the
point mass objects. Let the 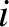 th object have mass
th object have mass 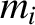 and displacement
and displacement
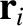 . Now, it is an experimentally verified fact that gravity is a superposable force. In other words, the gravitational force exerted
on object
. Now, it is an experimentally verified fact that gravity is a superposable force. In other words, the gravitational force exerted
on object 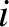 by object
by object 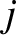 is unaffected by the presence of any other objects in the universe. Hence, the net gravitational
force experienced by object
is unaffected by the presence of any other objects in the universe. Hence, the net gravitational
force experienced by object 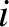 is
is
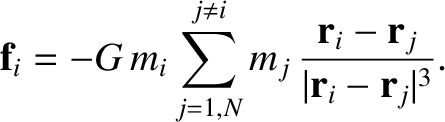 |
(1.240) |
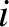 is missing from the sum on the right-hand side of the previous equation because
this object cannot exert a gravitational force on itself.
is missing from the sum on the right-hand side of the previous equation because
this object cannot exert a gravitational force on itself.
Suppose, finally, that a point object of mass 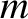 is located at the origin of our coordinate system. It follows from Equation (1.238)
that the gravitational acceleration, due to the gravitational attraction of mass
is located at the origin of our coordinate system. It follows from Equation (1.238)
that the gravitational acceleration, due to the gravitational attraction of mass 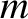 , experienced by another point object whose displacement is
, experienced by another point object whose displacement is 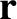 is
is