

Next: Gravitational Potential Theory
Up: Coupled Oscillations
Previous: Triatomic Molecule
- A particle of mass
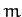 is attached to a rigid support by means of a spring of
spring constant
is attached to a rigid support by means of a spring of
spring constant 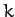 . At equilibrium, the spring hangs vertically
downward. An identical oscillator is added to this system, the
spring of the former being attached to the mass of the latter.
Calculate the characteristic frequencies for one-dimensional vertical
oscillations, and describe the associated normal modes.
. At equilibrium, the spring hangs vertically
downward. An identical oscillator is added to this system, the
spring of the former being attached to the mass of the latter.
Calculate the characteristic frequencies for one-dimensional vertical
oscillations, and describe the associated normal modes.
- A simple pendulum consists of a bob of mass
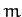 suspended
by an inextensible light string of length
suspended
by an inextensible light string of length 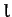 . From the bob of
this pendulum, a second identical
pendulum is suspended. Consider the case of small angle oscillations
in the same vertical plane. Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
. From the bob of
this pendulum, a second identical
pendulum is suspended. Consider the case of small angle oscillations
in the same vertical plane. Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
- A thin hoop of radius
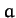 and mass
and mass 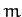 oscillates in its
own plane (which is constrained to be vertical) hanging from a single fixed point. A small mass
oscillates in its
own plane (which is constrained to be vertical) hanging from a single fixed point. A small mass 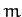 slides
without friction along the hoop. Consider the case of small oscillations.
Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
slides
without friction along the hoop. Consider the case of small oscillations.
Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
- A simple pendulum of mass
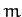 and length
and length 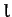 is suspended from
a block of mass
is suspended from
a block of mass 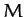 which is constrained to slide along a frictionless
horizontal track. Consider the case of small oscillations. Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
which is constrained to slide along a frictionless
horizontal track. Consider the case of small oscillations. Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
- A thin uniform rod of mass
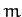 and length
and length 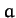 is suspended from
one end by a light string of length
is suspended from
one end by a light string of length 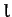 . The other end of the string
is attached to a fixed support. Consider the case of small oscillations
in a vertical plane.
Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
. The other end of the string
is attached to a fixed support. Consider the case of small oscillations
in a vertical plane.
Calculate the characteristic frequencies, and describe the associated normal modes.
- A triatomic molecule consists of three atoms of equal mass.
Each atom is attached to the other two atoms via identical chemical bonds.
The equilibrium state of the molecule is such that the masses are at the vertices of
an equilateral triangle of side
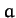 . Modeling the chemical bonds as
springs of spring constant
. Modeling the chemical bonds as
springs of spring constant 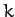 , and only considering motion in the plane of the molecule, find the vibrational frequencies and normal modes of the molecule. Exclude translational and rotational modes.
, and only considering motion in the plane of the molecule, find the vibrational frequencies and normal modes of the molecule. Exclude translational and rotational modes.


Next: Gravitational Potential Theory
Up: Coupled Oscillations
Previous: Triatomic Molecule
Richard Fitzpatrick
2011-03-31