

Next: 1-d problem with Dirichlet
Up: Poisson's equation
Previous: Poisson's equation
In this section, we shall discuss some simple numerical techniques for
solving Poisson's equation:
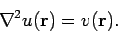 |
(108) |
Here, 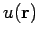 is usually some sort of potential, whereas
is usually some sort of potential, whereas 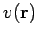 is a
source term.
The solution to the above equation is generally required in some simply-connected volume
is a
source term.
The solution to the above equation is generally required in some simply-connected volume 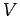 bounded by a
closed surface
bounded by a
closed surface 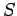 . There are two main types of boundary conditions to Poisson's equation.
In so-called Dirichlet boundary conditions, the potential
. There are two main types of boundary conditions to Poisson's equation.
In so-called Dirichlet boundary conditions, the potential 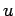 is specified on the bounding
surface
is specified on the bounding
surface 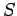 . In so-called Neumann boundary conditions, the normal gradient of the
potential
. In so-called Neumann boundary conditions, the normal gradient of the
potential
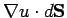 is specified on the bounding surface.
is specified on the bounding surface.
Poisson's equation is of particular importance in electrostatics and Newtonian gravity.
In electrostatics, we can write the electric field 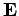 in terms of an electric
potential
in terms of an electric
potential 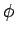 :
:
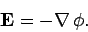 |
(109) |
The potential itself satisfies Poisson's equation:
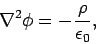 |
(110) |
where 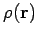 is the charge density, and
is the charge density, and 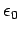 the permittivity of
free-space. In Newtonian gravity, we can write the force
the permittivity of
free-space. In Newtonian gravity, we can write the force 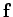 exerted on a
unit test mass in terms of a gravitational potential
exerted on a
unit test mass in terms of a gravitational potential 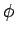 :
:
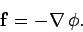 |
(111) |
The potential satisfies Poisson's equation:
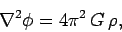 |
(112) |
where 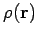 is the mass density, and
is the mass density, and 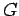 the universal gravitational
constant.
the universal gravitational
constant.


Next: 1-d problem with Dirichlet
Up: Poisson's equation
Previous: Poisson's equation
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-03-29
![]() in terms of an electric
potential
in terms of an electric
potential ![]() :
: