

Next: Circular motion
Up: Conservation of momentum
Previous: Worked example 6.5: Elastic
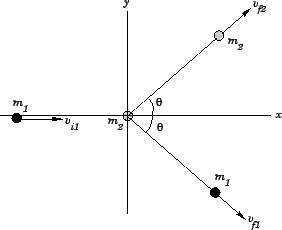
Question: Two objects slide over a frictionless
horizontal surface. The first object, mass
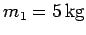 , is propelled with
speed
, is propelled with
speed
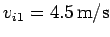 toward the second object, mass
toward the second object, mass
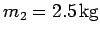 , which is initially at rest. After the collision, both
objects have velocities which are directed
, which is initially at rest. After the collision, both
objects have velocities which are directed
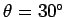 on either side of the
original line of motion of the first object. What are the
final speeds of the two objects? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
on either side of the
original line of motion of the first object. What are the
final speeds of the two objects? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
Answer: Let us adopt the coordinate system shown in the diagram. Conservation
of momentum along the 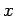 -axis yields
-axis yields
Likewise, conservation of momentum along the 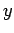 -axis yields
-axis yields
The above pair of equations can be combined to give
and
The initial kinetic energy of the system is
The final kinetic energy of the system is
Since 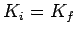 , the collision is elastic.
, the collision is elastic.


Next: Circular motion
Up: Conservation of momentum
Previous: Worked example 6.5: Elastic
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-02-02

![]() -axis yields
-axis yields