

Next: Motion with constant acceleration
Up: Motion in 3 dimensions
Previous: Vector velocity and vector
An object moving in 3 dimensions with constant velocity 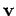 possesses
a vector displacement of the form
possesses
a vector displacement of the form
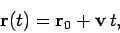 |
(61) |
where the constant vector 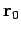 is the displacement at time
is the displacement at time 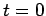 . Note
that
. Note
that
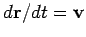 and
and
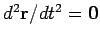 , as expected.
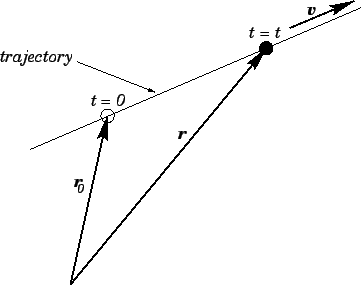
As illustrated in Fig. 14, the object's trajectory is a straight-line
which passes through point
, as expected.
As illustrated in Fig. 14, the object's trajectory is a straight-line
which passes through point 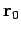 at time
at time 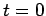 and runs parallel to vector
and runs parallel to vector
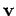 .
.
Figure 14:
Motion with constant velocity
 |
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-02-02