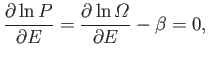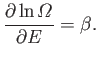

Next: Spin-1/2 Paramagnetism
Up: Applications of Statistical Thermodynamics
Previous: Introduction
Canonical Probability Distribution
We have gained some understanding of the macroscopic properties of the
air in a classroom (say). For instance, we know
something about its internal energy and specific heat capacity.
How can we obtain information about the
statistical properties of the molecules that make
up this air? Consider a specific molecule. It constantly collides with
its immediate neighbor molecules,
and occasionally bounces off the walls of the room. These
interactions ``inform'' it about the macroscopic state of the air,
such as its temperature, pressure, and volume. The
statistical distribution of the molecule over its own particular microstates must
be consistent with this macrostate. In other words, if we have a large group
of such molecules with similar statistical distributions
then they must be equivalent to
air with the appropriate macroscopic properties. So, it ought to be possible
to calculate the probability distribution of the molecule over its microstates
from a knowledge of these macroscopic properties.
We can think of the interaction of a molecule with the
air in a classroom as
analogous to the interaction of a small system,  , in thermal contact with a
heat reservoir,
, in thermal contact with a
heat reservoir, 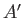 . The air acts like a heat reservoir because its energy
fluctuations due to interactions
with the molecule are far too small to affect any
of its macroscopic parameters. Let us
determine the probability,
. The air acts like a heat reservoir because its energy
fluctuations due to interactions
with the molecule are far too small to affect any
of its macroscopic parameters. Let us
determine the probability, 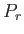 , of finding system
, of finding system 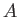 in one particular
microstate,
in one particular
microstate, 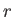 , of energy
, of energy 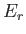 , when it is thermal equilibrium with the heat
reservoir,
, when it is thermal equilibrium with the heat
reservoir, 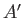 .
.
As usual, we assume fairly weak interaction between 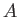 and
and 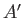 , so that
the energies of these two systems
are additive. The energy of
, so that
the energies of these two systems
are additive. The energy of 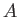 is not known at this
stage. In fact, only the total energy of the combined system,
is not known at this
stage. In fact, only the total energy of the combined system,
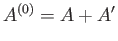 , is known. Suppose that the
total energy lies in the range
, is known. Suppose that the
total energy lies in the range 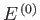 to
to
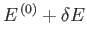 .
The overall energy is constant in time, because
.
The overall energy is constant in time, because 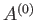 is assumed to be an isolated system, so
is assumed to be an isolated system, so
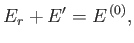 |
(7.1) |
where 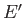 denotes the energy of the reservoir
denotes the energy of the reservoir 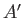 . Let
. Let
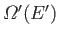 be the
number of microstates accessible to the reservoir when its energy lies in the
range
be the
number of microstates accessible to the reservoir when its energy lies in the
range 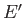 to
to
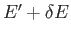 . Clearly, if system
. Clearly, if system 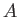 has an energy
has an energy 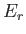 then
the reservoir
then
the reservoir 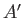 must have an energy close to
must have an energy close to
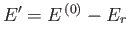 . Hence,
because
. Hence,
because 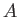 is in one definite state (i.e., state
is in one definite state (i.e., state 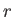 ), and the total
number of states accessible to
), and the total
number of states accessible to 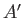 is
is
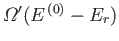 , it
follows that
the total number
of states accessible to the combined system is simply
, it
follows that
the total number
of states accessible to the combined system is simply
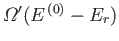 .
The principle of equal a priori probabilities tells us the probability
of occurrence of a particular situation is proportional to the number
of accessible microstates. Thus,
.
The principle of equal a priori probabilities tells us the probability
of occurrence of a particular situation is proportional to the number
of accessible microstates. Thus,
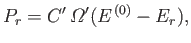 |
(7.2) |
where 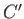 is a constant of proportionality that is independent of
is a constant of proportionality that is independent of 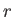 .
This constant can be determined by the normalization condition
.
This constant can be determined by the normalization condition
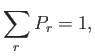 |
(7.3) |
where the sum is over all possible states of system 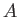 , irrespective of their energy.
, irrespective of their energy.
Let us now make use of the fact that system 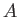 is far smaller than system
is far smaller than system 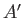 .
It follows that
.
It follows that
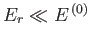 , so the slowly-varying logarithm of
, so the slowly-varying logarithm of 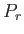 can be Taylor expanded about
can be Taylor expanded about
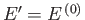 . Thus,
. Thus,
![$\displaystyle \ln P_r = \ln C' +\ln {\mit\Omega}'(E^{ (0)}) -\left[\frac{\partial \ln {\mit\Omega}'} {\partial E'} \right]_0 E_r +\cdots.$](img1287.png) |
(7.4) |
Note that we must expand 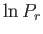 , rather than
, rather than 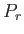 itself, because the latter
function varies so rapidly with energy
that the radius of convergence of its Taylor series
is too small for the series to be of any practical use.
The higher-order terms in Equation (7.4) can be safely
neglected, because
itself, because the latter
function varies so rapidly with energy
that the radius of convergence of its Taylor series
is too small for the series to be of any practical use.
The higher-order terms in Equation (7.4) can be safely
neglected, because
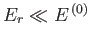 . Now, the derivative
. Now, the derivative
![$\displaystyle \left[\frac{\partial \ln {\mit\Omega}'}{\partial E'} \right]_0 \equiv \beta$](img1288.png) |
(7.5) |
is evaluated at the fixed energy
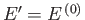 , and is, thus, a constant, independent
of the energy,
, and is, thus, a constant, independent
of the energy, 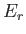 , of
, of 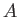 . In fact, we know, from Chapter 5, that this derivative
is just the
temperature parameter
. In fact, we know, from Chapter 5, that this derivative
is just the
temperature parameter
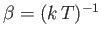 characterizing the heat
reservoir
characterizing the heat
reservoir 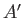 . Here,
. Here, 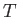 is the absolute temperature of the reservoir. Hence, Equation (7.4) becomes
is the absolute temperature of the reservoir. Hence, Equation (7.4) becomes
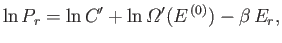 |
(7.6) |
giving
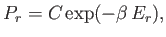 |
(7.7) |
where 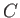 is a constant independent of
is a constant independent of 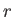 . The parameter
. The parameter 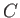 is determined by
the normalization condition, which gives
is determined by
the normalization condition, which gives
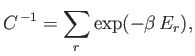 |
(7.8) |
so that the distribution becomes
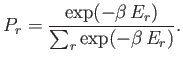 |
(7.9) |
This distribution is known as the canonical probability distribution (it is also sometimes called the Boltzmann probability distribution), and is an extremely important result in statistical physics.
The canonical distribution often causes confusion. People who are familiar with the
principle of equal a priori probabilities, which says that all microstates
are equally probable, are understandably surprised when they come across the
canonical distribution, which says that high energy microstates are markedly less
probable then low energy states. However, there is no need for any
confusion. The principle of equal a priori probabilities applies to
the whole system, whereas the canonical distribution only applies to
a small part of the system. The two results are perfectly consistent.
If the small system is in a microstate with a comparatively high energy, 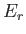 , then
the remainder of the system (i.e., the reservoir) has a slightly lower energy,
, then
the remainder of the system (i.e., the reservoir) has a slightly lower energy, 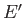 , than
usual (because the overall energy is fixed). The number of accessible microstates
of the reservoir is a very strongly increasing function of its energy. It
follows that if the small system has a
high energy then significantly less states
than usual are accessible to the reservoir, so the number of microstates
accessible
to the overall system is reduced, and, hence, the configuration is comparatively
unlikely. The strong increase in the number of accessible microstates of the
reservoir with increasing
, than
usual (because the overall energy is fixed). The number of accessible microstates
of the reservoir is a very strongly increasing function of its energy. It
follows that if the small system has a
high energy then significantly less states
than usual are accessible to the reservoir, so the number of microstates
accessible
to the overall system is reduced, and, hence, the configuration is comparatively
unlikely. The strong increase in the number of accessible microstates of the
reservoir with increasing 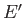 gives rise to the strong (i.e., exponential) decrease
in the likelihood of a state
gives rise to the strong (i.e., exponential) decrease
in the likelihood of a state 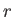 of the small system with increasing
of the small system with increasing 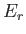 .
The exponential factor
.
The exponential factor
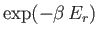 is called the Boltzmann factor.
is called the Boltzmann factor.
The canonical distribution gives the probability of finding the small system 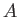 in one particular state
in one particular state 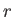 of energy
of energy 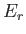 . The probability
. The probability
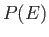 that
that 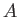 has an energy in the small range between
has an energy in the small range between 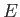 and
and
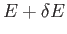 is just the sum of all the probabilities of the states that lie in this
range. However, because each of these states has approximately the same Boltzmann
factor, this sum can be written
is just the sum of all the probabilities of the states that lie in this
range. However, because each of these states has approximately the same Boltzmann
factor, this sum can be written
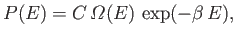 |
(7.10) |
where
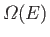 is the number of microstates of
is the number of microstates of 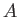 whose energies lie
in the appropriate
range. Suppose that system
whose energies lie
in the appropriate
range. Suppose that system 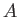 is itself a large system, but still very
much smaller than system
is itself a large system, but still very
much smaller than system 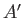 . For a large system, we expect
. For a large system, we expect
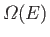 to
be a very rapidly increasing function of energy, so the probability
to
be a very rapidly increasing function of energy, so the probability 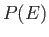 is the product of a rapidly increasing function of
is the product of a rapidly increasing function of 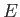 , and another
rapidly decreasing
function (i.e., the Boltzmann factor). This gives a sharp
maximum of
, and another
rapidly decreasing
function (i.e., the Boltzmann factor). This gives a sharp
maximum of 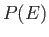 at some particular value of the energy. As system
at some particular value of the energy. As system 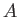 becomes larger,
this maximum becomes sharper. Eventually, the maximum becomes so sharp
that the energy of system
becomes larger,
this maximum becomes sharper. Eventually, the maximum becomes so sharp
that the energy of system 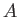 is almost bound to lie at the most probable energy.
As usual, the most probable energy is evaluated by looking for the maximum of
is almost bound to lie at the most probable energy.
As usual, the most probable energy is evaluated by looking for the maximum of
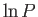 , so
, so
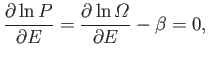 |
(7.11) |
giving
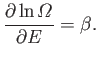 |
(7.12) |
Of course, this corresponds to the situation in which the temperature
of  is the same as that of the reservoir. This is a result that we
have seen before. (See Chapter 5.) Note, however, that the canonical
distribution is applicable no matter how small system
is the same as that of the reservoir. This is a result that we
have seen before. (See Chapter 5.) Note, however, that the canonical
distribution is applicable no matter how small system  is, so
it is a far more
general result than any that we have previously obtained.
is, so
it is a far more
general result than any that we have previously obtained.


Next: Spin-1/2 Paramagnetism
Up: Applications of Statistical Thermodynamics
Previous: Introduction
Richard Fitzpatrick
2016-01-25
![]() , in thermal contact with a
heat reservoir,
, in thermal contact with a
heat reservoir, ![]() . The air acts like a heat reservoir because its energy
fluctuations due to interactions
with the molecule are far too small to affect any
of its macroscopic parameters. Let us
determine the probability,
. The air acts like a heat reservoir because its energy
fluctuations due to interactions
with the molecule are far too small to affect any
of its macroscopic parameters. Let us
determine the probability, ![]() , of finding system
, of finding system ![]() in one particular
microstate,
in one particular
microstate, ![]() , of energy
, of energy ![]() , when it is thermal equilibrium with the heat
reservoir,
, when it is thermal equilibrium with the heat
reservoir, ![]() .
.
![]() and
and ![]() , so that
the energies of these two systems
are additive. The energy of
, so that
the energies of these two systems
are additive. The energy of ![]() is not known at this
stage. In fact, only the total energy of the combined system,
is not known at this
stage. In fact, only the total energy of the combined system,
![]() , is known. Suppose that the
total energy lies in the range
, is known. Suppose that the
total energy lies in the range ![]() to
to
![]() .
The overall energy is constant in time, because
.
The overall energy is constant in time, because ![]() is assumed to be an isolated system, so
is assumed to be an isolated system, so
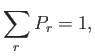
![]() is far smaller than system
is far smaller than system ![]() .
It follows that
.
It follows that
![]() , so the slowly-varying logarithm of
, so the slowly-varying logarithm of ![]() can be Taylor expanded about
can be Taylor expanded about
![]() . Thus,
. Thus,
![$\displaystyle \left[\frac{\partial \ln {\mit\Omega}'}{\partial E'} \right]_0 \equiv \beta$](img1288.png)
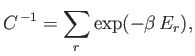
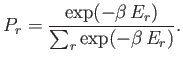
![]() , then
the remainder of the system (i.e., the reservoir) has a slightly lower energy,
, then
the remainder of the system (i.e., the reservoir) has a slightly lower energy, ![]() , than
usual (because the overall energy is fixed). The number of accessible microstates
of the reservoir is a very strongly increasing function of its energy. It
follows that if the small system has a
high energy then significantly less states
than usual are accessible to the reservoir, so the number of microstates
accessible
to the overall system is reduced, and, hence, the configuration is comparatively
unlikely. The strong increase in the number of accessible microstates of the
reservoir with increasing
, than
usual (because the overall energy is fixed). The number of accessible microstates
of the reservoir is a very strongly increasing function of its energy. It
follows that if the small system has a
high energy then significantly less states
than usual are accessible to the reservoir, so the number of microstates
accessible
to the overall system is reduced, and, hence, the configuration is comparatively
unlikely. The strong increase in the number of accessible microstates of the
reservoir with increasing ![]() gives rise to the strong (i.e., exponential) decrease
in the likelihood of a state
gives rise to the strong (i.e., exponential) decrease
in the likelihood of a state ![]() of the small system with increasing
of the small system with increasing ![]() .
The exponential factor
.
The exponential factor
![]() is called the Boltzmann factor.
is called the Boltzmann factor.
![]() in one particular state
in one particular state ![]() of energy
of energy ![]() . The probability
. The probability
![]() that
that ![]() has an energy in the small range between
has an energy in the small range between ![]() and
and
![]() is just the sum of all the probabilities of the states that lie in this
range. However, because each of these states has approximately the same Boltzmann
factor, this sum can be written
is just the sum of all the probabilities of the states that lie in this
range. However, because each of these states has approximately the same Boltzmann
factor, this sum can be written