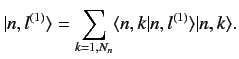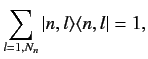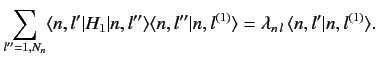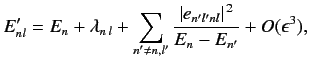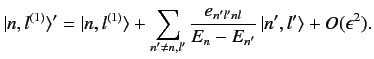

Next: Linear Stark Effect
Up: Time-Independent Perturbation Theory
Previous: Quadratic Stark Effect
Degenerate Perturbation Theory
Let us now consider systems in which the eigenstates of
the unperturbed Hamiltonian, 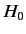 , possess
degenerate energy levels. It is always possible to
represent degenerate energy eigenstates
as the simultaneous eigenstates
of the Hamiltonian and some other Hermitian operator (or group
of operators). Let us denote this operator (or group of operators)
, possess
degenerate energy levels. It is always possible to
represent degenerate energy eigenstates
as the simultaneous eigenstates
of the Hamiltonian and some other Hermitian operator (or group
of operators). Let us denote this operator (or group of operators) 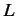 .
We can write
.
We can write
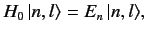 |
(647) |
and
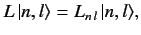 |
(648) |
where
![$ [H_0, L] = 0$](img1544.png) . Here, the
. Here, the 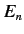 and the
and the 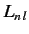 are real numbers that
depend on the quantum numbers
are real numbers that
depend on the quantum numbers 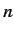 , and
, and 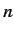 and
and 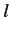 , respectively.
It is always possible
to find a sufficient number of operators which commute with the Hamiltonian
in order to ensure
that the
, respectively.
It is always possible
to find a sufficient number of operators which commute with the Hamiltonian
in order to ensure
that the 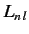 are all different. In other words, we can
choose
are all different. In other words, we can
choose 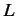 such that the quantum numbers
such that the quantum numbers
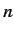 and
and 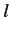 uniquely specify each eigenstate. Suppose that for each value
of
uniquely specify each eigenstate. Suppose that for each value
of 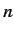 there are
there are 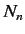 different values of
different values of 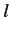 : i.e., the
: i.e., the 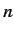 th energy eigenstate
is
th energy eigenstate
is 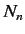 -fold degenerate.
-fold degenerate.
In general, 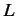 does not commute with the perturbing Hamiltonian,
does not commute with the perturbing Hamiltonian, 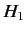 .
This implies that the modified energy eigenstates are not eigenstates
of
.
This implies that the modified energy eigenstates are not eigenstates
of 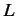 . In this situation, we expect the perturbation to split the degeneracy
of the energy levels, so that each modified eigenstate
. In this situation, we expect the perturbation to split the degeneracy
of the energy levels, so that each modified eigenstate
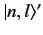 acquires
a unique energy eigenvalue
acquires
a unique energy eigenvalue 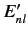 . Let us naively attempt to use the standard
perturbation theory of Section 7.3 to evaluate the modified
energy eigenstates
and energy levels. A direct generalization of Equations (614) and (615) yields
. Let us naively attempt to use the standard
perturbation theory of Section 7.3 to evaluate the modified
energy eigenstates
and energy levels. A direct generalization of Equations (614) and (615) yields
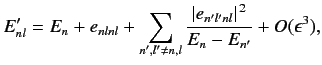 |
(649) |
and
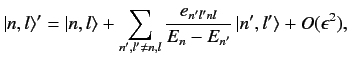 |
(650) |
where
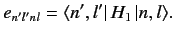 |
(651) |
It is fairly obvious that the summations in Equations (649) and (650) are not
well-behaved if the 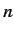 th energy level is degenerate. The problem terms
are those involving unperturbed eigenstates labeled by the same value of
th energy level is degenerate. The problem terms
are those involving unperturbed eigenstates labeled by the same value of 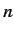 , but different
values of
, but different
values of 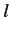 : i.e., those states whose unperturbed energies are
: i.e., those states whose unperturbed energies are 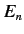 . These
terms give rise to singular factors
. These
terms give rise to singular factors
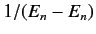 in the summations.
Note, however, that this problem would not exist if the matrix
elements,
in the summations.
Note, however, that this problem would not exist if the matrix
elements, 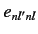 , of the perturbing Hamiltonian between distinct,
degenerate, unperturbed energy eigenstates
corresponding to the eigenvalue
, of the perturbing Hamiltonian between distinct,
degenerate, unperturbed energy eigenstates
corresponding to the eigenvalue 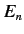 were zero. In other words, if
were zero. In other words, if
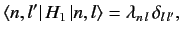 |
(652) |
then all of the singular terms in Equations (649) and (650) would vanish.
In general, Equation (652) is not satisfied. Fortunately, we can always redefine
the unperturbed energy eigenstates belonging to the eigenvalue 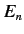 in such
a manner that Equation (652) is satisfied. Let us define
in such
a manner that Equation (652) is satisfied. Let us define 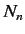 new states
that are linear combinations of the
new states
that are linear combinations of the 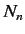 original degenerate
eigenstates corresponding
to the eigenvalue
original degenerate
eigenstates corresponding
to the eigenvalue 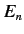 :
:
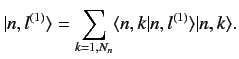 |
(653) |
Note that these new states are also degenerate energy eigenstates
of the unperturbed Hamiltonian corresponding to the eigenvalue 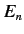 .
The
.
The
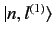 are chosen in
such a manner that they are eigenstates of the perturbing
Hamiltonian,
are chosen in
such a manner that they are eigenstates of the perturbing
Hamiltonian, 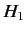 . Thus,
. Thus,
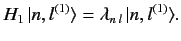 |
(654) |
The
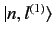 are also chosen so that they are orthogonal,
and have unit lengths.
It follows that
are also chosen so that they are orthogonal,
and have unit lengths.
It follows that
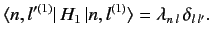 |
(655) |
Thus, if we use the new eigenstates, instead of the old ones, then we can employ
Equations (649) and (650) directly, because all of the singular terms vanish.
The only remaining difficulty is to determine the new eigenstates in terms of
the original ones.
Now
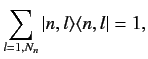 |
(656) |
where 1 denotes the identity operator in the sub-space of all unperturbed
energy eigenkets corresponding to the eigenvalue 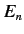 . Using this completeness
relation, the operator eigenvalue equation (654) can be transformed into a
straightforward matrix eigenvalue equation:
. Using this completeness
relation, the operator eigenvalue equation (654) can be transformed into a
straightforward matrix eigenvalue equation:
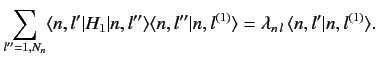 |
(657) |
This can be written more transparently as
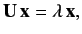 |
(658) |
where the elements of the
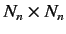 Hermitian matrix
Hermitian matrix 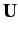 are
are
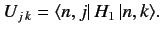 |
(659) |
Provided that the determinant of 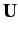 is non-zero, Equation (658) can always be solved to
give
is non-zero, Equation (658) can always be solved to
give 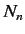 eigenvalues
eigenvalues
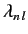 (for
(for 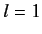 to
to 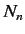 ), with
), with
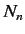 corresponding eigenvectors
corresponding eigenvectors
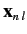 . The eigenvectors specify the
weights of the new eigenstates in terms of the original eigenstates: i.e.,
. The eigenvectors specify the
weights of the new eigenstates in terms of the original eigenstates: i.e.,
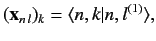 |
(660) |
for 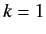 to
to 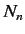 . In our new scheme, Equations (649) and (650) yield
. In our new scheme, Equations (649) and (650) yield
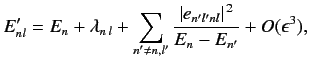 |
(661) |
and
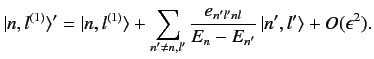 |
(662) |
There are no singular terms in these expressions, because the summations
are over 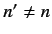 : i.e., they specifically exclude
the problematic,
degenerate, unperturbed energy eigenstates corresponding to the eigenvalue
: i.e., they specifically exclude
the problematic,
degenerate, unperturbed energy eigenstates corresponding to the eigenvalue 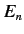 .
Note that the first-order energy-shifts are equivalent to the eigenvalues
of the matrix equation, (658).
.
Note that the first-order energy-shifts are equivalent to the eigenvalues
of the matrix equation, (658).


Next: Linear Stark Effect
Up: Time-Independent Perturbation Theory
Previous: Quadratic Stark Effect
Richard Fitzpatrick
2013-04-08
![]() does not commute with the perturbing Hamiltonian,
does not commute with the perturbing Hamiltonian, ![]() .
This implies that the modified energy eigenstates are not eigenstates
of
.
This implies that the modified energy eigenstates are not eigenstates
of ![]() . In this situation, we expect the perturbation to split the degeneracy
of the energy levels, so that each modified eigenstate
. In this situation, we expect the perturbation to split the degeneracy
of the energy levels, so that each modified eigenstate
![]() acquires
a unique energy eigenvalue
acquires
a unique energy eigenvalue ![]() . Let us naively attempt to use the standard
perturbation theory of Section 7.3 to evaluate the modified
energy eigenstates
and energy levels. A direct generalization of Equations (614) and (615) yields
. Let us naively attempt to use the standard
perturbation theory of Section 7.3 to evaluate the modified
energy eigenstates
and energy levels. A direct generalization of Equations (614) and (615) yields
![]() in such
a manner that Equation (652) is satisfied. Let us define
in such
a manner that Equation (652) is satisfied. Let us define ![]() new states
that are linear combinations of the
new states
that are linear combinations of the ![]() original degenerate
eigenstates corresponding
to the eigenvalue
original degenerate
eigenstates corresponding
to the eigenvalue ![]() :
: