Wave Polarization
A pure right-handed circularly polarized wave propagating along the
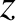 -axis takes the form
In terms of complex amplitudes, this becomes
-axis takes the form
In terms of complex amplitudes, this becomes
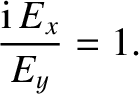 |
(5.58) |
Similarly, a left-handed circularly polarized wave is characterized by
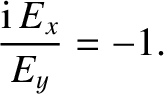 |
(5.59) |
The polarization of the transverse electric field is obtained from the
middle line of Equation (5.42):
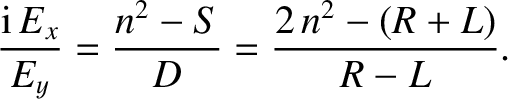 |
(5.60) |
For the case of parallel propagation, with 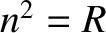 , the previous formula
yields
, the previous formula
yields
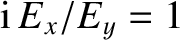 . Similarly, for the case of parallel propagation,
with
. Similarly, for the case of parallel propagation,
with 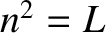 , we obtain
, we obtain
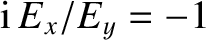 . Thus, it is clear that
the roots
. Thus, it is clear that
the roots 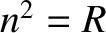 and
and 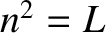 in Equations (5.51)–(5.53) correspond to
right- and left-handed circularly polarized waves, respectively.
in Equations (5.51)–(5.53) correspond to
right- and left-handed circularly polarized waves, respectively.
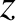 -axis takes the form
-axis takes the form
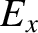
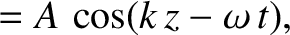
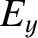
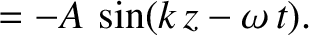
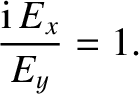
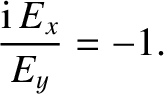
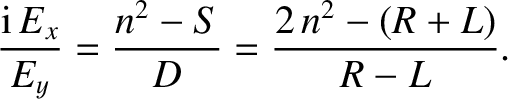
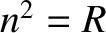 , the previous formula
yields
, the previous formula
yields
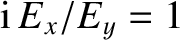 . Similarly, for the case of parallel propagation,
with
. Similarly, for the case of parallel propagation,
with 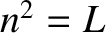 , we obtain
, we obtain
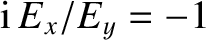 . Thus, it is clear that
the roots
. Thus, it is clear that
the roots 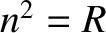 and
and 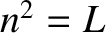 in Equations (5.51)–(5.53) correspond to
right- and left-handed circularly polarized waves, respectively.
in Equations (5.51)–(5.53) correspond to
right- and left-handed circularly polarized waves, respectively.