Next: Exercises Up: Plasma Parameters Previous: Plasma Beta Contents
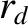 , becomes comparable, or less than,
the de Broglie wavelength,
, becomes comparable, or less than,
the de Broglie wavelength,
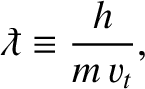 |
(1.37) |
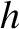 is Planck's constant. According to Equations (1.3) and (1.16), the condition
is Planck's constant. According to Equations (1.3) and (1.16), the condition
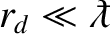 is equivalent to
A plasma that satisfies this condition is said to be degenerate, whereas a plasma that does not is said to be non-degenerate. The behavior of degenerate plasmas is fundamentally different to that
of the non-degenerate plasmas discussed in this book (because the former plasmas are governed by quantum mechanics, whereas the latter
are
governed by classical mechanics). It can be seen that if both species have comparable temperatures then the condition, given in Equation (1.38), for
degeneracy is more easily satisfied by the electrons than by the ions. Moreover, it is evident that degenerate plasmas tend to be cold and dense, whereas
non-degenerate plasmas are generally hot and diffuse. (See Haas 2011 for a comprehensive discussion of degenerate plasmas.)
is equivalent to
A plasma that satisfies this condition is said to be degenerate, whereas a plasma that does not is said to be non-degenerate. The behavior of degenerate plasmas is fundamentally different to that
of the non-degenerate plasmas discussed in this book (because the former plasmas are governed by quantum mechanics, whereas the latter
are
governed by classical mechanics). It can be seen that if both species have comparable temperatures then the condition, given in Equation (1.38), for
degeneracy is more easily satisfied by the electrons than by the ions. Moreover, it is evident that degenerate plasmas tend to be cold and dense, whereas
non-degenerate plasmas are generally hot and diffuse. (See Haas 2011 for a comprehensive discussion of degenerate plasmas.)
It is actually possible for quantum effects to modify collisions in non-degenerate plasmas that satisfy the inequality
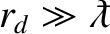 . In fact, the
criterion for quantum effects not to modify collisions is
. In fact, the
criterion for quantum effects not to modify collisions is
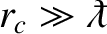 , where
, where 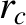 is the mean distance of closest approach during
collisions. However, it follows from Equation (1.20) that
is the mean distance of closest approach during
collisions. However, it follows from Equation (1.20) that
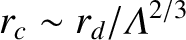 . Hence, the
criterion for classical collisions becomes
. Hence, the
criterion for classical collisions becomes
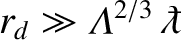 . In a weakly coupled plasma, for
which
. In a weakly coupled plasma, for
which
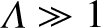 , this
criterion is harder to satisfy that the criterion,
, this
criterion is harder to satisfy that the criterion,
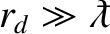 , for non-degeneracy.
, for non-degeneracy.