Next: Parallactic inequality Up: Lunar motion Previous: Variation
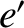 .
.
According to Equations (11.135) and (11.147),
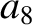 |
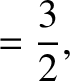 |
(11.231) |
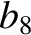 |
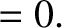 |
(11.232) |
According to Equations (11.136) and (11.148),
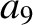 |
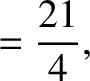 |
(11.235) |
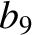 |
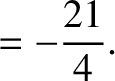 |
(11.236) |
Finally, according to Equations (11.137) and (11.149),
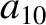 |
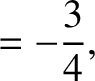 |
(11.239) |
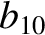 |
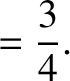 |
(11.240) |
It follows from Equations (11.122)–(11.124), (11.167)–(11.169), and (11.179)–(11.181), as well as the previous expressions for 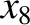 ,
, 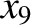 ,
, 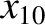 ,
, 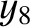 ,
, 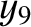 , and
, and 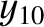 , that the net perturbation of the lunar orbit
due to terms in the solution of the lunar equations of motion that depend linearly on
, that the net perturbation of the lunar orbit
due to terms in the solution of the lunar equations of motion that depend linearly on 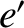 is
is
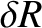 |
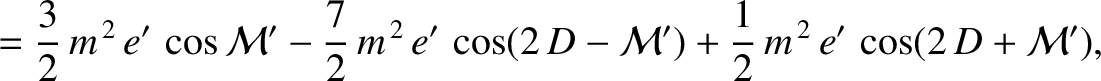 |
(11.243) |
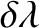 |
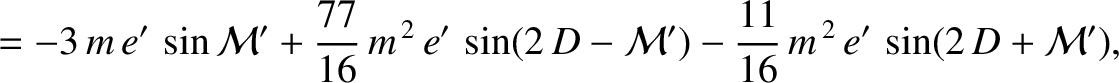 |
(11.244) |
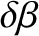 |
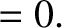 |
(11.245) |
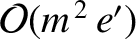 .
.
The first term on the right-hand side of Equation (11.244) is known as the annual equation, and is caused by a combination of the perturbing action of the Sun and the
slight eccentricity (
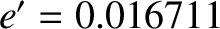 ) of the apparent solar orbit about the Earth–Moon barycenter. The annual equation attains its maximum amplitude when the Earth (or, rather, the Earth–Moon barycenter) is halfway between its perihelion and its
aphelion points (i.e., when
) of the apparent solar orbit about the Earth–Moon barycenter. The annual equation attains its maximum amplitude when the Earth (or, rather, the Earth–Moon barycenter) is halfway between its perihelion and its
aphelion points (i.e., when
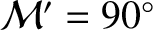 or
or 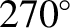 ). Conversely, the amplitude of the annual equation is zero when the Earth passes through its perihelion or its aphelion points (i.e., when
). Conversely, the amplitude of the annual equation is zero when the Earth passes through its perihelion or its aphelion points (i.e., when
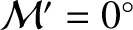 or
or 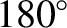 ).
According to Equation (11.244), the annual equation generates a perturbation in the lunar ecliptic longitude that oscillates with a period
of a solar year, and has an amplitude (calculated using
).
According to Equation (11.244), the annual equation generates a perturbation in the lunar ecliptic longitude that oscillates with a period
of a solar year, and has an amplitude (calculated using
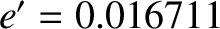 and
and 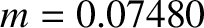 ) of
) of 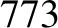 arc seconds. As before, the oscillation period is in good agreement with
observations, whereas the amplitude is somewhat inaccurate [it should be
arc seconds. As before, the oscillation period is in good agreement with
observations, whereas the amplitude is somewhat inaccurate [it should be 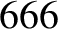 arc seconds (Chapront-Touzé and Chapront 1988)] because of the
omission of higher-order (in
arc seconds (Chapront-Touzé and Chapront 1988)] because of the
omission of higher-order (in 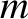 and
and 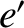 ) contributions.
) contributions.