- What values would a measurement of
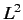 yield, and with
what probabilities?
yield, and with
what probabilities?
- Same for
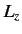 .
.
- Same for
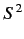 .
.
- Same for
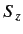 .
.
- Same for
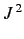 .
.
- Same for
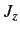 .
.
- What is the probability density for finding the electron at
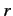 ,
, 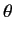 ,
, 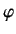 ?
?
- What is the probability density for finding the electron in the
spin up state (with respect to the
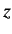 -axis) at radius
-axis) at radius 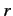 ?
?
![$\displaystyle V({\bf x}) = V_1(r) + V_2(r)\left[3\,\frac{(\mbox{\boldmath $\sig...
...\right] + V_3(r)\,\mbox{\boldmath $\sigma$}_n\cdot\mbox{\boldmath $\sigma$}_p,
$](img1424.png)
where
- In the spin singlet (i.e., spin zero) state.
- In the spin triplet (i.e., spin one) state.
- If a measurement of the spin of one of the electrons shows that it
is in the state with
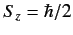 , what is the probability that a
measurement of the
, what is the probability that a
measurement of the 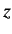 -component of the spin of the
other electron yields
-component of the spin of the
other electron yields
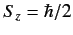 ?
?
- If a measurement of the spin of one of the electrons shows
that it is in the state with
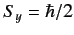 , what is the probability that a
measurement of the
, what is the probability that a
measurement of the 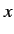 -component of the spin of the
other electron yields
-component of the spin of the
other electron yields
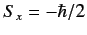 ?
?
- Finally, if electron 1 is in a spin state described by
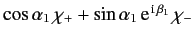 , and
electron 2 is in a spin state described by
, and
electron 2 is in a spin state described by
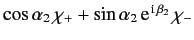 , what is
the probability that the two-electron spin state is a triplet (i.e., spin one) state?
, what is
the probability that the two-electron spin state is a triplet (i.e., spin one) state?