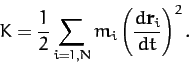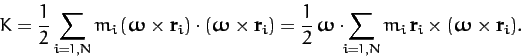

Next: Matrix Eigenvalue Theory
Up: Rigid Body Rotation
Previous: Moment of Inertia Tensor
The instantaneous rotational kinetic energy of a rotating rigid body is written
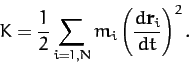 |
(467) |
Making use of Equation (457), and some vector identities (see Section A.9),
the kinetic energy takes the form
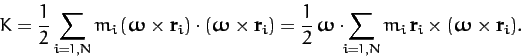 |
(468) |
Hence, it follows from (458) that
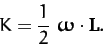 |
(469) |
Making use of Equation (466), we can also
write
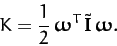 |
(470) |
Here,
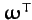 is the row vector of the Cartesian components
is the row vector of the Cartesian components
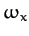 ,
, 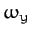 ,
, 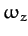 , which is, of course, the transpose
(denoted
, which is, of course, the transpose
(denoted 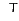 ) of the column vector
) of the column vector 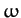 .
When written in component form, the above equation yields
.
When written in component form, the above equation yields
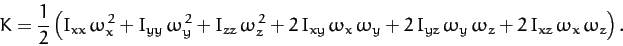 |
(471) |
Richard Fitzpatrick
2011-03-31