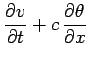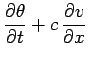

Next: The 1-d advection equation
Up: The wave equation
Previous: The wave equation
The wave equation, which in one dimension takes the form
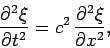 |
(230) |
occurs so frequently in physics that it is not necessary to enumerate examples.
Here, 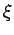 is usually some sort of displacement or perturbation, whereas
is usually some sort of displacement or perturbation, whereas 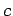 is the
(constant) wave speed. The wave equation possesses the formal solution
is the
(constant) wave speed. The wave equation possesses the formal solution
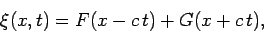 |
(231) |
where 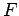 and
and 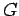 are arbitrary functions. The above solution represents arbitrarily
shaped wave pulses propagating with speed
are arbitrary functions. The above solution represents arbitrarily
shaped wave pulses propagating with speed 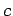 in the
in the 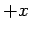 and
and 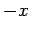 directions, respectively, without
changing shape.
directions, respectively, without
changing shape.
The wave equation, which is second-order in space and time,
can be written as two coupled first-order equations
by defining the new variables
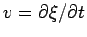 and
and
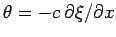 .
Expressing Eq. (230) in terms of these new variables, we obtain
.
Expressing Eq. (230) in terms of these new variables, we obtain
Note that when solving the wave equation numerically it is generally preferable to write it
as a set of coupled first-order equations, as shown above.


Next: The 1-d advection equation
Up: The wave equation
Previous: The wave equation
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-03-29
![]() and
and
![]() .
Expressing Eq. (230) in terms of these new variables, we obtain
.
Expressing Eq. (230) in terms of these new variables, we obtain