

Next: The vertical pendulum
Up: Circular motion
Previous: The conical pendulum
Non-uniform circular motion
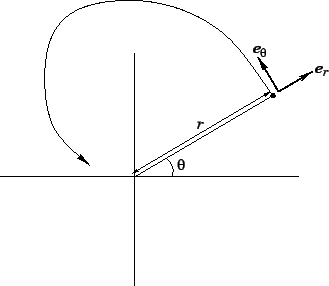
Consider an object which executes non-uniform circular motion, as shown in Fig. 61.
Suppose that the motion is confined to a 2-dimensional plane. We can specify the
instantaneous position of the object in terms of its polar coordinates 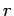 and
and
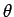 . Here,
. Here, 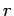 is the radial distance of the object from the origin, whereas
is the radial distance of the object from the origin, whereas 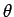 is the angular bearing of the object from the origin, measured with respect to some arbitrarily chosen
direction. We imagine that both
is the angular bearing of the object from the origin, measured with respect to some arbitrarily chosen
direction. We imagine that both 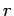 and
and 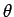 are changing in time. As an example of
non-uniform circular motion, consider the motion of the Earth around the Sun. Suppose that
the origin of our coordinate system corresponds to the position of the Sun. As the Earth rotates, its
angular bearing
are changing in time. As an example of
non-uniform circular motion, consider the motion of the Earth around the Sun. Suppose that
the origin of our coordinate system corresponds to the position of the Sun. As the Earth rotates, its
angular bearing 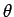 , relative to the Sun, obviously changes in time.
However, since the
Earth's orbit is slightly elliptical, its radial distance
, relative to the Sun, obviously changes in time.
However, since the
Earth's orbit is slightly elliptical, its radial distance 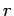 from the
Sun also varies in time. Moreover, as the Earth moves closer to the Sun, its rate of
rotation speeds up, and vice versa. Hence, the rate of change of
from the
Sun also varies in time. Moreover, as the Earth moves closer to the Sun, its rate of
rotation speeds up, and vice versa. Hence, the rate of change of 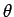 with
time is non-uniform.
with
time is non-uniform.
Figure 61:
Polar coordinates.
 |
Let us define two unit vectors, 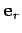 and
and
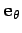 . Incidentally,
a unit vector simply a vector whose length is unity.
As shown in Fig. 61, the radial
unit vector
. Incidentally,
a unit vector simply a vector whose length is unity.
As shown in Fig. 61, the radial
unit vector 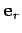 always points from the origin to the instantaneous position of the object.
Moreover, the tangential unit vector
always points from the origin to the instantaneous position of the object.
Moreover, the tangential unit vector
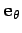 is always normal
to
is always normal
to 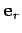 , in the direction of increasing
, in the direction of increasing 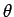 . The position vector
. The position vector 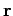 of the object can be written
of the object can be written
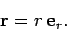 |
(270) |
In other words, vector 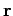 points in the same direction as the radial unit vector
points in the same direction as the radial unit vector
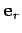 , and is of
length
, and is of
length 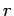 . We can write the object's velocity in the form
. We can write the object's velocity in the form
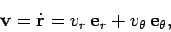 |
(271) |
whereas the acceleration is written
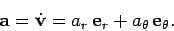 |
(272) |
Here, 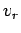 is termed the object's radial velocity, whilst
is termed the object's radial velocity, whilst 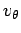 is
termed the tangential velocity. Likewise,
is
termed the tangential velocity. Likewise, 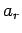 is the radial acceleration,
and
is the radial acceleration,
and 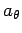 is the tangential acceleration. But, how do we express these
quantities in terms of the object's polar coordinates
is the tangential acceleration. But, how do we express these
quantities in terms of the object's polar coordinates 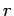 and
and 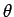 ? It turns out that this
is a far from straightforward task. For instance, if we simply differentiate Eq. (270)
with respect to time, we obtain
? It turns out that this
is a far from straightforward task. For instance, if we simply differentiate Eq. (270)
with respect to time, we obtain
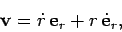 |
(273) |
where 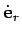 is the time derivative of the radial unit vector--this quantity
is non-zero because
is the time derivative of the radial unit vector--this quantity
is non-zero because 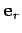 changes direction as the object moves. Unfortunately,
it is not entirely clear how to evaluate
changes direction as the object moves. Unfortunately,
it is not entirely clear how to evaluate 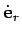 . In the following, we
outline a famous trick for calculating
. In the following, we
outline a famous trick for calculating 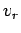 ,
, 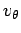 , etc. without
ever having to evaluate the time derivatives of the unit vectors
, etc. without
ever having to evaluate the time derivatives of the unit vectors
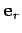 and
and
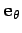 .
.
Consider a general complex number,
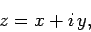 |
(274) |
where 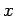 and
and 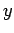 are real, and
are real, and 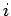 is the square root of
is the square root of 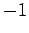 (i.e.,
(i.e., 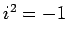 ).
Here,
).
Here, 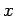 is the real part of
is the real part of 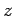 , whereas
, whereas 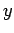 is the imaginary part.
We can visualize
is the imaginary part.
We can visualize 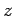 as a point in the so-called complex plane: i.e., a 2-dimensional
plane
in which the real parts of complex numbers are plotted along one Cartesian axis, whereas the
corresponding imaginary parts are plotted along the other axis.
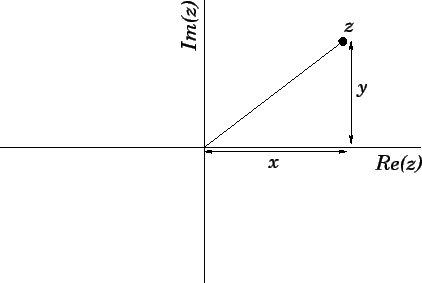
Thus, the coordinates
of
as a point in the so-called complex plane: i.e., a 2-dimensional
plane
in which the real parts of complex numbers are plotted along one Cartesian axis, whereas the
corresponding imaginary parts are plotted along the other axis.
Thus, the coordinates
of 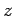 in the complex plane are simply (
in the complex plane are simply (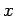 ,
, 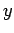 ). See Fig. 62. In other words,
we can use a complex number to represent a position vector in a 2-dimensional plane.
Note that the length of the vector is equal to the modulus of the corresponding complex
number. Incidentally, the modulus of
). See Fig. 62. In other words,
we can use a complex number to represent a position vector in a 2-dimensional plane.
Note that the length of the vector is equal to the modulus of the corresponding complex
number. Incidentally, the modulus of 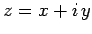 is defined
is defined
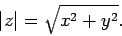 |
(275) |
Figure 62:
Representation of a complex number in the complex plane.
 |
Consider the complex number
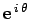 , where
, where 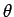 is real.
A famous result in complex analysis--known as de Moivre's theorem--allows us
to split this number into its real and imaginary components:
is real.
A famous result in complex analysis--known as de Moivre's theorem--allows us
to split this number into its real and imaginary components:
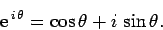 |
(276) |
Now, as we have just discussed, we can think of
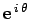 as representing a vector
in the complex plane: the real and imaginary parts of
as representing a vector
in the complex plane: the real and imaginary parts of
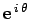 form the coordinates of the head of the vector, whereas the tail of the vector
corresponds to the origin. What are the properties of this vector? Well,
the length of the vector is given by
form the coordinates of the head of the vector, whereas the tail of the vector
corresponds to the origin. What are the properties of this vector? Well,
the length of the vector is given by
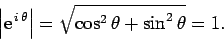 |
(277) |
In other words,
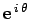 represents a unit vector.
In fact, it is clear from Fig. 63 that
represents a unit vector.
In fact, it is clear from Fig. 63 that
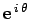 represents
the radial unit vector
represents
the radial unit vector 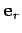 for an object whose angular polar
coordinate (measured anti-clockwise from the real axis) is
for an object whose angular polar
coordinate (measured anti-clockwise from the real axis) is 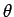 .
Can we also find a complex representation of the corresponding tangential
unit vector
.
Can we also find a complex representation of the corresponding tangential
unit vector
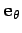 ? Actually, we can. The
complex number
? Actually, we can. The
complex number
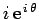 can be written
can be written
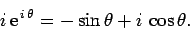 |
(278) |
Here, we have just multiplied Eq. (276) by 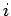 , making use of the fact
that
, making use of the fact
that 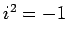 . This number again represents a unit vector, since
. This number again represents a unit vector, since
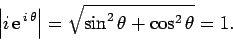 |
(279) |
Moreover, as is clear from Fig. 63, this vector is normal to 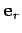 , in the
direction of increasing
, in the
direction of increasing 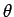 . In other words,
. In other words,
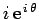 represents
the tangential unit vector
represents
the tangential unit vector
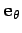 .
.
Figure 63:
Representation of the unit vectors 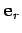 and
and
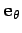 in the complex plane.
in the complex plane.
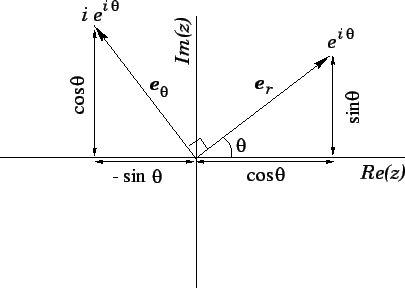 |
Consider an object executing non-uniform circular motion in the complex plane. By analogy
with Eq. (270), we can represent the instantaneous position vector of
this object via the complex number
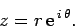 |
(280) |
Here, 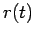 is the object's radial distance from the origin, whereas
is the object's radial distance from the origin, whereas 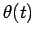 is its angular bearing relative to the real axis. Note that, in the above formula, we are using
is its angular bearing relative to the real axis. Note that, in the above formula, we are using
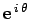 to represent the radial unit vector
to represent the radial unit vector 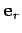 . Now,
if
. Now,
if 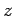 represents the position vector of the object, then
represents the position vector of the object, then
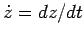 must
represent the object's velocity vector. Differentiating Eq. (280) with
respect to time, using the standard rules of calculus, we obtain
must
represent the object's velocity vector. Differentiating Eq. (280) with
respect to time, using the standard rules of calculus, we obtain
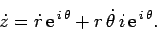 |
(281) |
Comparing with Eq. (271), recalling that
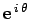 represents
represents 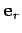 and
and
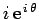 represents
represents
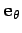 , we obtain
, we obtain
where
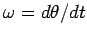 is the object's instantaneous angular velocity. Thus,
as desired,
we have obtained expressions for the radial and tangential velocities of the
object in terms of its polar coordinates,
is the object's instantaneous angular velocity. Thus,
as desired,
we have obtained expressions for the radial and tangential velocities of the
object in terms of its polar coordinates, 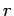 and
and 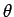 .
We can go further. Let us differentiate
.
We can go further. Let us differentiate 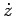 with respect to time,
in order to obtain a complex number representing the object's vector
acceleration. Again, using the standard rules of calculus, we obtain
with respect to time,
in order to obtain a complex number representing the object's vector
acceleration. Again, using the standard rules of calculus, we obtain
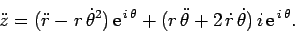 |
(284) |
Comparing with Eq. (272), recalling that
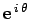 represents
represents 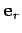 and
and
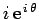 represents
represents
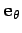 , we obtain
, we obtain
Thus, we now have expressions for the object's radial and tangential accelerations in terms
of 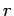 and
and 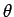 . The beauty of this derivation is that the complex analysis
has automatically taken care of the fact that the unit vectors
. The beauty of this derivation is that the complex analysis
has automatically taken care of the fact that the unit vectors
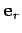 and
and
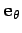 change direction as the object moves.
change direction as the object moves.
Let us now consider the commonly occurring special case in which an object executes a circular
orbit at fixed radius, but varying angular velocity. Since the radius is fixed, it follows
that
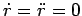 . According to Eqs. (282) and (283), the radial
velocity of the object is zero, and the tangential velocity takes the form
. According to Eqs. (282) and (283), the radial
velocity of the object is zero, and the tangential velocity takes the form
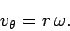 |
(287) |
Note that the above equation is exactly the same as Eq. (250)--the only difference
is that we have now proved that this relation holds for non-uniform, as well as uniform,
circular motion.
According to Eq. (285), the radial acceleration is given by
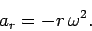 |
(288) |
The minus sign indicates that this acceleration is directed towards the centre of the
circle. Of course, the above equation is equivalent to Eq. (259)--the only difference
is that we have now proved that this relation holds for non-uniform, as well as uniform,
circular motion. Finally, according to Eq. (286), the tangential acceleration
takes the form
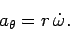 |
(289) |
The existence of a non-zero tangential acceleration (in the former case) is the one difference between
non-uniform and uniform circular motion (at constant radius).


Next: The vertical pendulum
Up: Circular motion
Previous: The conical pendulum
Richard Fitzpatrick
2006-02-02

![]() and
and
![]() . Incidentally,
a unit vector simply a vector whose length is unity.
As shown in Fig. 61, the radial
unit vector
. Incidentally,
a unit vector simply a vector whose length is unity.
As shown in Fig. 61, the radial
unit vector ![]() always points from the origin to the instantaneous position of the object.
Moreover, the tangential unit vector
always points from the origin to the instantaneous position of the object.
Moreover, the tangential unit vector
![]() is always normal
to
is always normal
to ![]() , in the direction of increasing
, in the direction of increasing ![]() . The position vector
. The position vector ![]() of the object can be written
of the object can be written
![]() , where
, where ![]() is real.
A famous result in complex analysis--known as de Moivre's theorem--allows us
to split this number into its real and imaginary components:
is real.
A famous result in complex analysis--known as de Moivre's theorem--allows us
to split this number into its real and imaginary components:
![]() . According to Eqs. (282) and (283), the radial
velocity of the object is zero, and the tangential velocity takes the form
. According to Eqs. (282) and (283), the radial
velocity of the object is zero, and the tangential velocity takes the form