

Next: Determination of Lunar-Solar Elongation
Up: Lunar-Solar Syzygies and Eclipses
Previous: Lunar-Solar Syzygies and Eclipses
Let 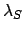 and
and 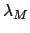 represent the ecliptic longitudes
of the sun and the moon, respectively. The lunar-solar elongation is defined
represent the ecliptic longitudes
of the sun and the moon, respectively. The lunar-solar elongation is defined
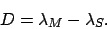 |
(132) |
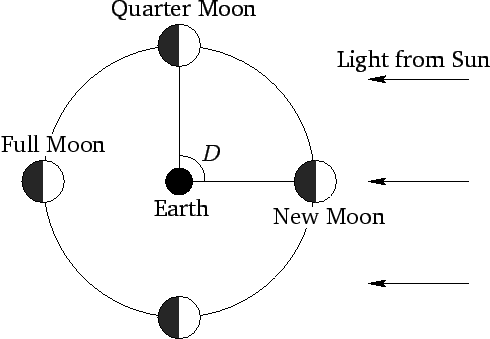
Since the moon is only visible because of light reflected from the sun, there is a fairly obvious relationship between lunar-solar elongation and lunar
phase--see Fig. 26. For instance, a new moon corresponds to
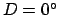 , a quarter moon to
, a quarter moon to 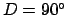 or
or 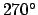 , and a full moon to
, and a full moon to 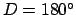 . New moons and full moons are collectively known as lunar-solar syzygies.
. New moons and full moons are collectively known as lunar-solar syzygies.
Figure 26:
The phases of the moon.
 |
Richard Fitzpatrick
2010-07-21