Next: Variation Up: Lunar motion Previous: Useful definitions
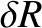 |
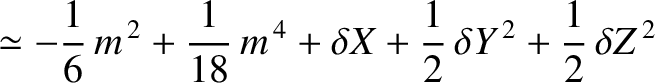 |
(11.113) |
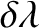 |
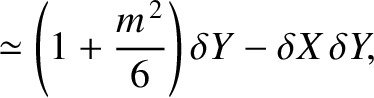 |
(11.114) |
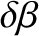 |
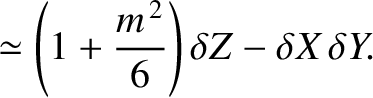 |
(11.115) |
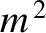 ,
, 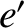 ,
, 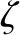 ,
, 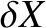 ,
, 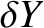 , and
, and 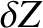 .
.
Let us write
Here, the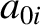 ,
, 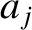 ,
, 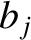 ,
, 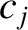 , et cetera, are
, et cetera, are
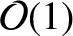 constants.
constants.
Equations (11.110)–(11.124) can be combined to give
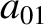 |
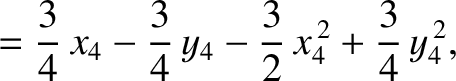 |
(11.125) |
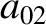 |
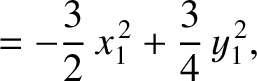 |
(11.126) |
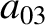 |
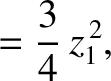 |
(11.127) |
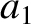 |
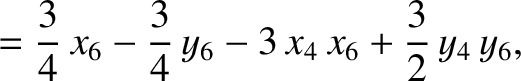 |
(11.128) |
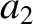 |
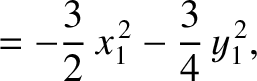 |
(11.129) |
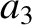 |
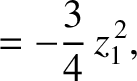 |
(11.130) |
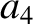 |
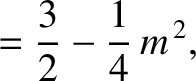 |
(11.131) |
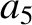 |
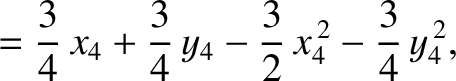 |
(11.132) |
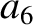 |
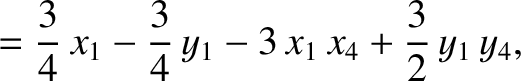 |
(11.133) |
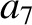 |
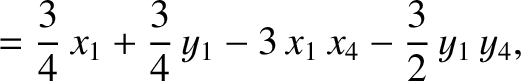 |
(11.134) |
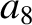 |
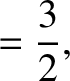 |
(11.135) |
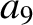 |
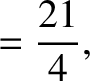 |
(11.136) |
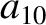 |
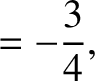 |
(11.137) |
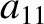 |
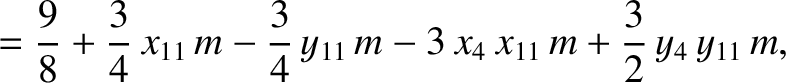 |
(11.138) |
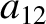 |
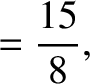 |
(11.139) |
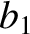 |
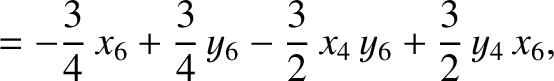 |
(11.140) |
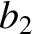 |
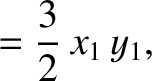 |
(11.141) |
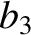 |
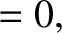 |
(11.142) |
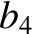 |
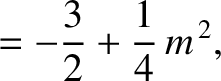 |
(11.143) |
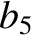 |
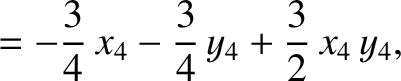 |
(11.144) |
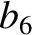 |
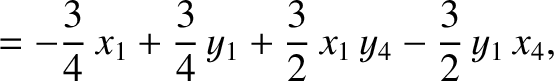 |
(11.145) |
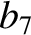 |
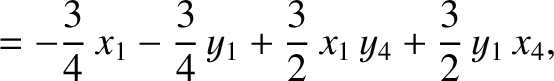 |
(11.146) |
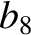 |
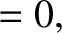 |
(11.147) |
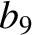 |
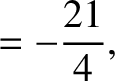 |
(11.148) |
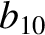 |
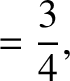 |
(11.149) |
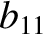 |
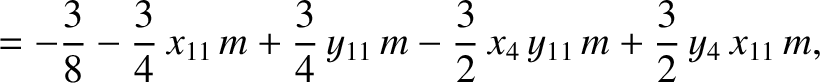 |
(11.150) |
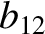 |
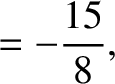 |
(11.151) |
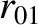 |
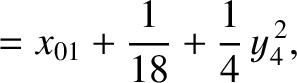 |
(11.157) |
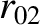 |
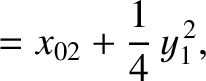 |
(11.158) |
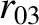 |
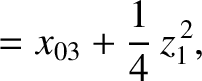 |
(11.159) |
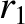 |
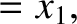 |
(11.160) |
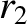 |
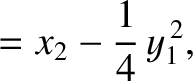 |
(11.161) |
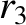 |
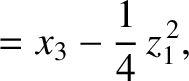 |
(11.162) |
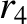 |
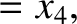 |
(11.163) |
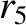 |
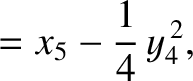 |
(11.164) |
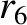 |
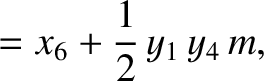 |
(11.165) |
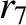 |
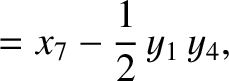 |
(11.166) |
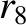 |
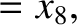 |
(11.167) |
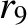 |
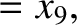 |
(11.168) |
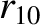 |
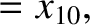 |
(11.169) |
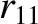 |
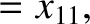 |
(11.170) |
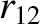 |
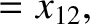 |
(11.171) |
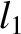 |
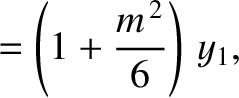 |
(11.172) |
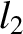 |
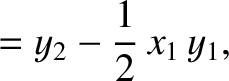 |
(11.173) |
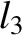 |
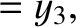 |
(11.174) |
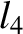 |
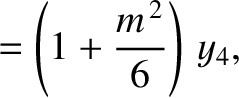 |
(11.175) |
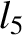 |
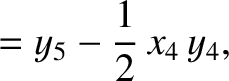 |
(11.176) |
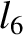 |
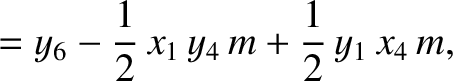 |
(11.177) |
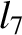 |
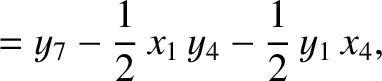 |
(11.178) |
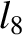 |
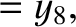 |
(11.179) |
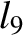 |
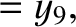 |
(11.180) |
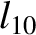 |
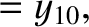 |
(11.181) |
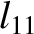 |
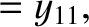 |
(11.182) |
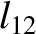 |
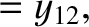 |
(11.183) |
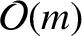 and
and
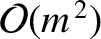 corrections to the parameters
corrections to the parameters 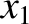 ,
, 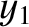 ,
, 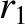 ,
, 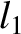 ,
, 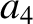 ,
, 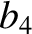 ,
, 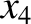 ,
, 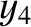 ,
, 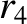 ,
, 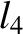 ,
, 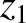 , and
, and 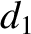 , and
, and
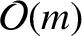 corrections to
the parameters
corrections to
the parameters 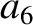 ,
, 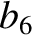 ,
, 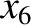 ,
, 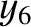 ,
, 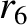 ,
, 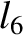 ,
, 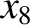 ,
, 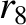 ,
, 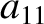 ,
, 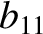 ,
, 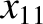 ,
, 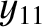 ,
, 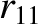 ,
, 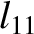 ,
, 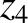 , and
, and 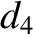 , while neglecting
similar corrections for all of the other parameters appearing in Equations (11.116)–(11.124).
, while neglecting
similar corrections for all of the other parameters appearing in Equations (11.116)–(11.124).
Substitution of Equations (11.116), (11.117), (11.119), and (11.120) into Equations (11.107) and (11.108) yields
for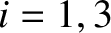 , as well as
as well as
for
, as well as
as well as
for 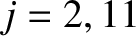 . In the previous two equations,
. In the previous two equations, 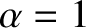 for
for
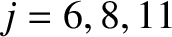 , and
, and 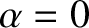 otherwise.
Moreover,
otherwise.
Moreover,
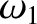 |
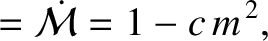 |
(11.194) |
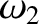 |
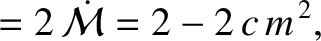 |
(11.195) |
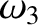 |
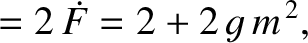 |
(11.196) |
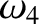 |
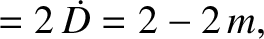 |
(11.197) |
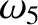 |
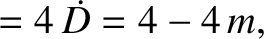 |
(11.198) |
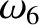 |
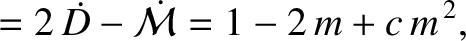 |
(11.199) |
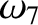 |
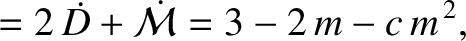 |
(11.200) |
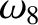 |
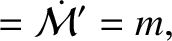 |
(11.201) |
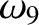 |
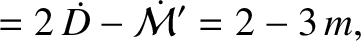 |
(11.202) |
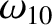 |
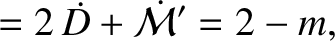 |
(11.203) |
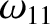 |
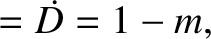 |
(11.204) |
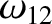 |
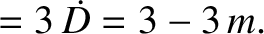 |
(11.205) |
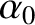 is an arbitrary constant, and
is an arbitrary constant, and 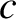 is an, as yet, unknown
is an, as yet, unknown
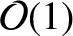 constant that parameterizes the precession of the lunar
perigee. Here, use has been made of the facts that
constant that parameterizes the precession of the lunar
perigee. Here, use has been made of the facts that 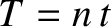 and
and 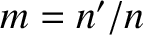 .
Likewise, we have assumed that the ecliptic longitude of the lunar ascending mode takes the form
where
.
Likewise, we have assumed that the ecliptic longitude of the lunar ascending mode takes the form
where 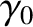 is an arbitrary constant, and
is an arbitrary constant, and 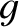 is an, as yet, unknown
is an, as yet, unknown
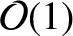 constant that parameterizes the regression of the lunar
ascending node.
constant that parameterizes the regression of the lunar
ascending node.
Substituting Equations (11.118) and (11.121) into Equation (11.109), we obtain
and for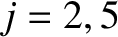 .
In the previous equation,
.
In the previous equation, 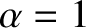 for
for 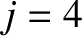 , and
, and 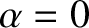 otherwise. Moreover,
otherwise. Moreover,
In the following few sections, we shall develop our solution of the lunar equations of motion in a systematic fashion by considering groups of similar terms separately.